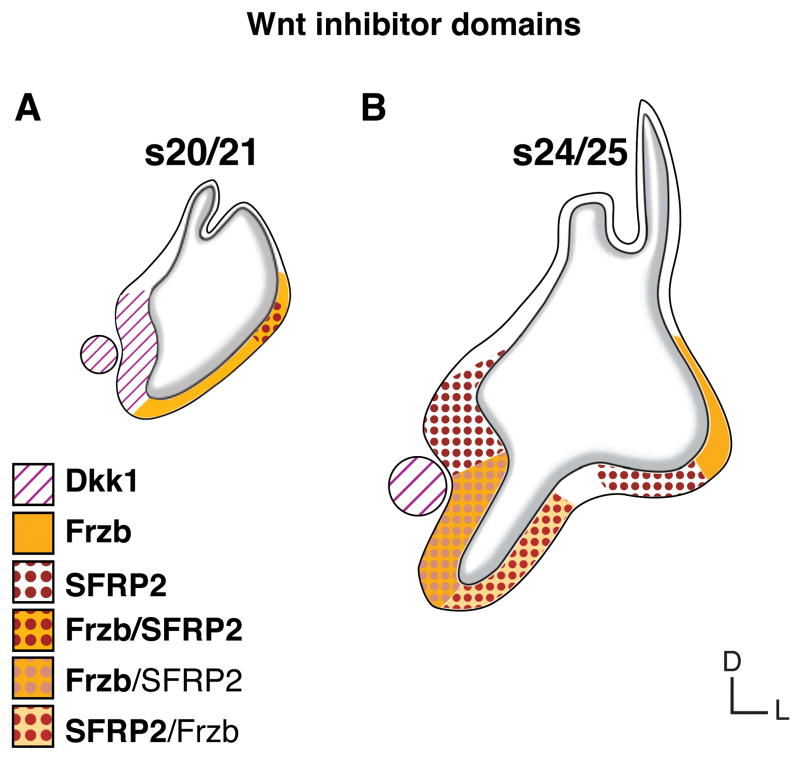
Fig. 6. Wnt inhibitor domains.
Comparison of two time points, A: otocyst stage 20/21 and B: inner ear primordium stage 24/25, reveals six differently composed Wnt inhibitor domains with distinct or overlapping expression of three Wnt inhibitor genes: (1) Dkk1 at s20 in the medial otocyst and SAG (circle); (2) Frzb at s20 in the lateral otocyst, and at s24/25 lateral-dorsal (in the vestibule); (3) co-expression of Frzb and SFRP2 at s20 in the lateral-dorsal otocyst; (4) SFRP2 at s24/25 in prosensory vestibular primordia; (5) co-expression with strong SFRP2 and mild Frzb at s24/25 lateral-ventral (in the nonsensory pars inferior); (6) co-expression with strong Frzb and mild SFRP2 at s24/25 medial-ventral (in the prosensory BP primordium). Not shown are the sporadic and weak expression of SFRP1 (see Fig. 2J) and an underlying broad expression of Dkk1 by s24/25 (Fig. 3E). Bold and plain font face in the legend refers to relative expression strength. Abbreviations: BP, basilar papilla; D, dorsal; L, lateral; s, embryonic stage; (SAG), statoacoustic ganglion.