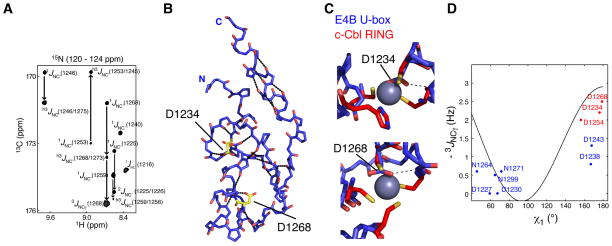
Figure 2. Identification of Hydrogen Bonds in E4B U-box by NMR Spectroscopy.
(A) A region from the constant time 3D J-HNCO NMR spectrum of E4B U-box showing peaks correlated through 1JNC’, 2JNC’, 3JNCγ and h3JNC’ scalar couplings.
(B) The nineteen H-bonds in E4B U-box that are listed in Table S3 were identified through h3JNC’ scalar coupling measurements. The dotted lines illustrate these H-bonds. Residues Asp1232 and Asp1268 for which side chain h3JNC’ scalar couplings were measured are shown. Asp1232 and Asp1268 correspond to the zinc binding regions of RING domains.
(C) Asp1232 and Asp1268 of E4B U-box approximately occupy the zinc centers (purple spheres) in c-Cbl RING domain (PDB entry 1FBV) when the U-box and RING domains are superimposed. H-bonds involving the two aspartate side chains were determined from h3JNC’ scalar coupling measurements and are shown by the dashed lines.
(D) Calibration curve for the dihedral angle (χ1) dependence of 3JNCγ scalar couplings in aspartate and asparagine residues. Blue and red points correlate experimental 3JNCγ and corresponding χ1 angle values from the crystal structure of E4B U-box. The red points correspond to residues for which a side chain carbonyl participates in a H-bond as determined from h3JNC scalar couplings.
See also Table S1 for the values of measured coupling constants.