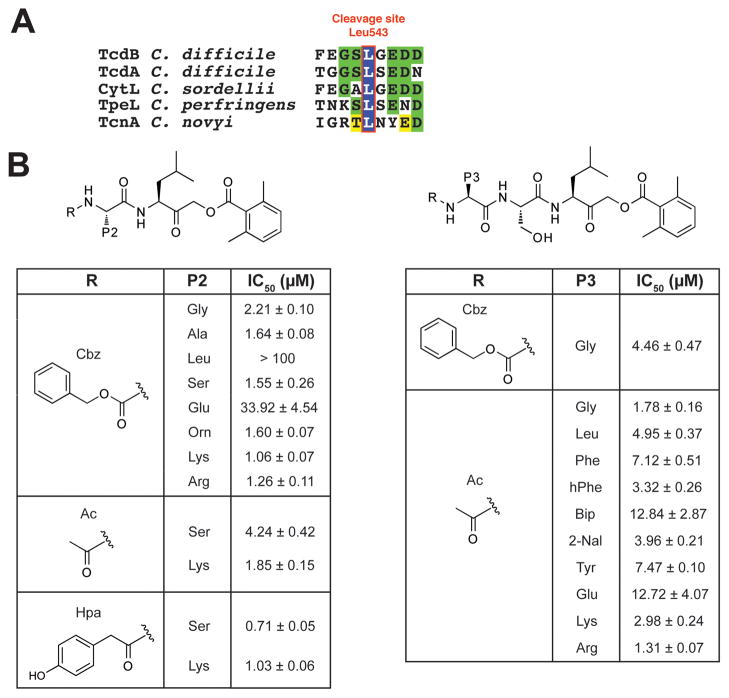
Figure 2. TcdB CPD rational inhibitor design and screening.
(A) Conserved substrate autocleavage site of C. difficile TcdB and related bacterial toxins. The toxin CPD cleaves after the highlighted leucine residue.
(B) Focused screen of capped di- and tripeptide covalent TcdB CPD inhibitors. Observed IC50 values were determined using the autocleavage assay for covalent AOMK inhibitors with diverse P2 (left) and P3 (right) residues. These compounds were N-terminally capped with carboxybenzyl (Cbz), acetyl (Ac), or hydroxyphenyl acetyl (Hpa) groups. The dipeptide inhibitor Hpa-SL-AOMK was found to be the most potent compound. Data represents the mean of three experiments ± standard deviation.
See also Figure S1.