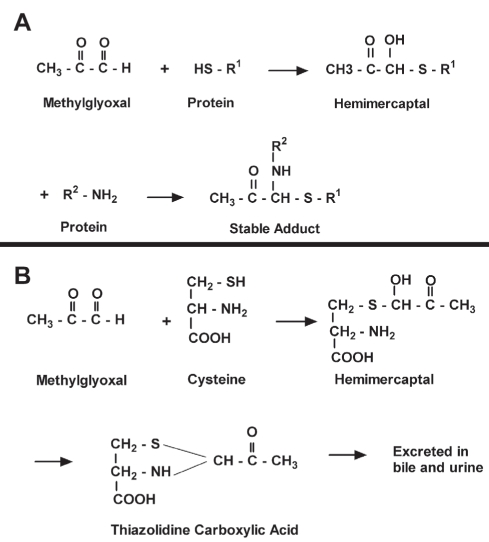
Figure 4).
A Reaction of methylglyoxal with the free sulfhydryl (HS or SH) group of a protein, with a further reaction with a free amino (NH2) group of protein forming a stable adduct, thus permanently altering its function. B Protective effect of endogenous cysteine from methylglyoxal by forming a thiazolidine-carboxylic acid derivative, which is excreted in bile and urine