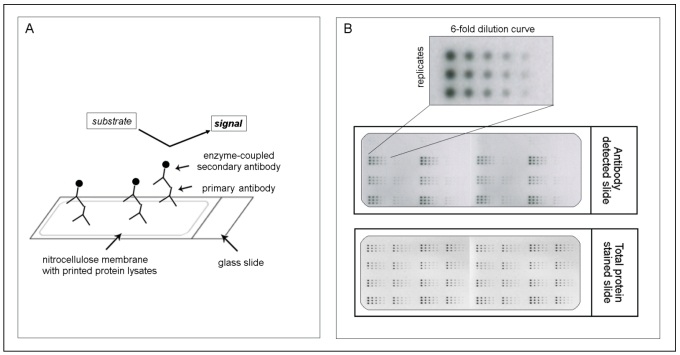
Figure 1.
The principle of reverse phase protein microarrays (RPPA): A: Protein lysates are spotted onto nitrocellulose-coated glass slides. Single proteins (e.g., PAI-1) can be detected by an antibody assay similar to a western blot analysis; a specific primary antibody binds to the spotted protein. After binding of an enzyme-coupled secondary antibody, protein expression can be measured by light- or fluorescence-based as well as colorimetric methods. B: Each sample is spotted in triplicate and in a six-step dilution series to ensure the quantitative measurement of the target protein in the linear detection range. The normalization of every antibody detected on the slide is performed using a total protein-stained slide (e.g., Sypro-Ruby protein stain).