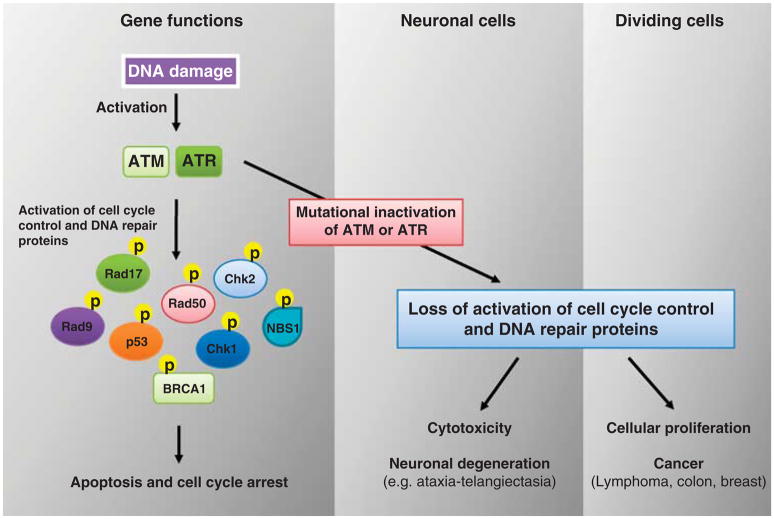
Figure 3.
Model of differential effects of ATM and ATR mutation in neuronal vs dividing somatic cells. In neurons, ATM/ATR loss-of-function manifests as cell death and neurodegeneration. In normally dividing cells such as epithelial cells, the same mutations can result in the accumulation of additional mutations with each successive generation, eventually resulting in cancer. Yellow circles labeled with P denotes phosphorylation. Abbreviations: ATM, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; ATR, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related; BRCA1, breast cancer 1; NBS1, nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 (nibrin); Rad17, RAD17 homolog.