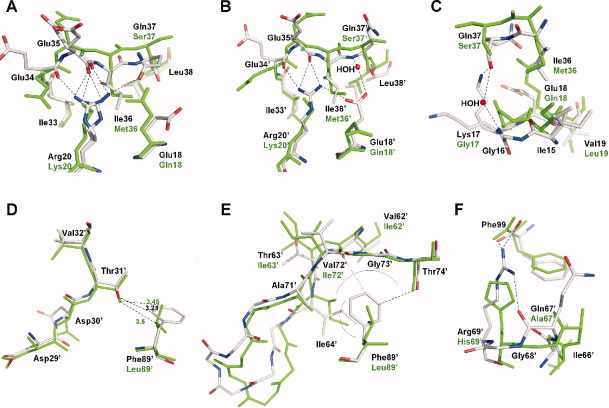
Figure 7.
Atomic descriptions of regions in the PR1N/DRV complex showing significant changes from the PR1M/DRV complex. The PR1N residues are colored by element type, whereas PR1M residues are colored green. The hydrogen bond and ion pair interactions are shown as broken lines. The PR1N residue positions are labeled in black, and the polymorphic differences in PR1M are labeled in green. A: Key deviations at the site of M36I substitution in the monomer A of PR1N/DRV complex. The M36I substitution causes part of the hinge loop to buckle inward, which is anchored by another polymorphic substitution K20R. Flexibility of monomer A is indicated by the alternate conformations of Arg20 and Glu35. B: The effect of M36I substitution in monomer B of PR1N/DRV. All the residues show single conformations, and the hinge loop is more tightly held in place by polymorphic substitution Glu18′, which forms an ion pair with Arg20′ and water-mediated hydrogen bond with the main-chain amide of Gln37′. Glu18′ also forms a total of six van der Waals interactions with Ile36′ and the main-chain carbonyl of Gln37′. C: The buckling of the hinge loop shifts Ile15 resulting in downward movement of the 10s loop. The carbonyl of Gly16 at the tip of the loop is flipped by 180°. D: Superposition of PR1N/DRV and PR1M/DRV structures at the site of L89′F substitution in monomer B. The L89′F substitution results in a shortened CH…O interaction with Thr31′ that induces a shift of ∼0.5 Å in the position of inhibitor-interacting residues Asp29′, Asp30′, and Val32′. E: Superposition of the 60s loops of PR1N/DRV and PR1M/DRV structures in monomer B. L89′F substitution in PR1N makes van der Waals interactions with Ile64′. The residues C-terminal to Ile 64′ in the 60s loop exhibit large deviations when compared with those of the PR1M/DRV structure. The other end of the loop is fixed by the extensive new interactions between Phe89′ and the main-chain atoms of Val72′ and Gly73′ and the carbonyl of Thr74′. The side chains of residues 65′–70′ are omitted for clarity. The van der Waals interactions are indicated by an arc. F: In addition to L89′F, the H69′R substitution is also responsible for the large deviations seen in the 60s loop. The H69′R is the only substitution with intersubunit interactions in PR1N and sits close to the tip of the loop. H69′R in monomer B forms ionic and van der Waals interactions with the C-terminal residue Phe99 in monomer A of PR1N/DRV complex.