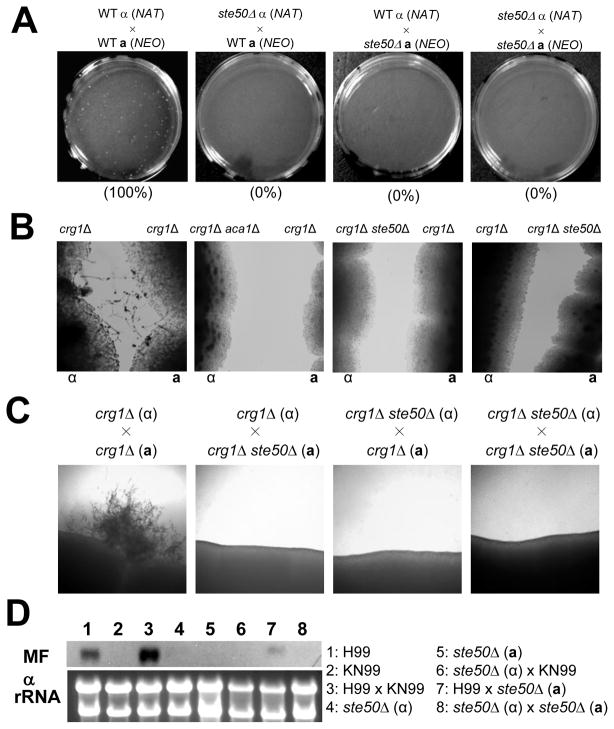
Fig. 6.
Ste50 governs sexual differentiation via the pheromone-responsive Cpk1 MAPK pathway. (A) Cell-cell fusion assays were performed with the following strains: WT α (NAT) × WT a (NEO) (YSB119 and YSB121), ste50Δ α (NAT) × WT a (NEO) (YSB317 and YSB121), WT α (NAT) × ste50Δ a (NEO) (YSB119 and YSB522), ste50Δ α (NAT) × ste50Δ a (NEO) (YSB317 and YSB522). Cell fusion efficiency for each experimental set was calculated relative to the control strains (WT α (NAT) × WT a (NEO)). (B) Confrontation assays were performed with the following strains: MATα crg1Δ (H99 crg1), MATa crg1Δ (PPW 196), MATα crg1Δ aca1Δ (YSB96), MATα crg1Δ ste50Δ (YSB632), and MATa crg1Δ ste50Δ (YSB637). Indicated strains were streaked in confrontation with each other on V8 agar medium and incubated at room temperature in the dark. Images were photographed after 10 days. (C) Mating reactions were initiated for the following strains: The crg1Δ ste50Δ double mutants showed mating defect in both unilateral crossing and bilateral crossing. crg1Δ α × crg1Δ a (H99 crg1 and PPW 196), crg1Δ α × crg1Δ ste50Δ a (H99 crg1 and YSB637), crg1Δ ste50Δ α × crg1Δ a (YSB632 and PPW 196), crg1Δ ste50Δ α × crg1Δ ste50Δ a (YSB632 and YSB637). The images were photographed after 12 days. (D) Northern blot analysis for monitoring pheromone gene expression was performed with total RNA isolated from solo- or co-cultures of the indicated strain(s) grown for 24 hr under mating conditions: WTα (H99), WTa (KN99a), ste50Δα (YSB317), and ste50Δa (YSB522). The blot was probed with the MFα1 gene.