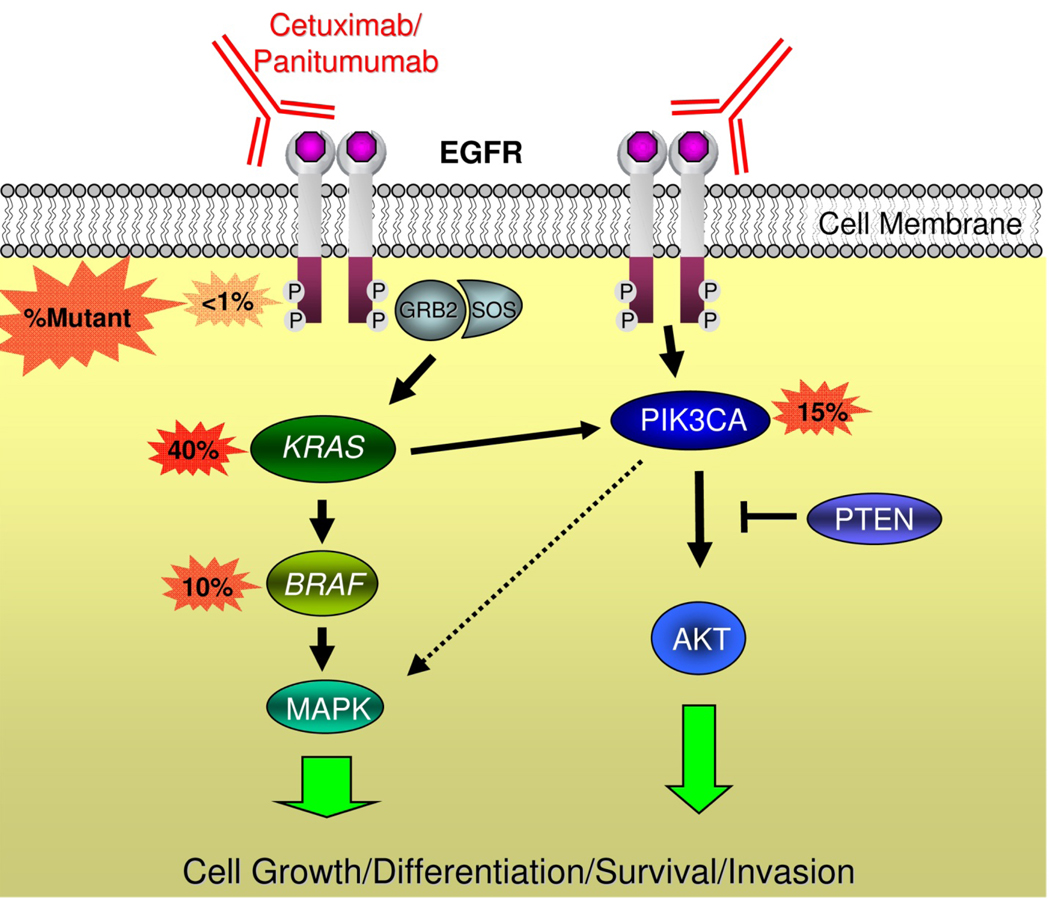
Figure 3. Mediators of EGFR signaling and anti-EGFR antibodies.
EGFR forms a homodimer after ligand activation, which results in phosphorylation/activation of the intra-cellular kinase domain and a cascade of downstream signaling including activation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK and phosphoinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathways that are associated with cell growth, differentiation, survival, and invasion. Monoclonal antibodies used to treat patients with metastatic colorectal cancer including cetuximab and panitumumab bind to the extracellular portion of EGFR and inhibit signaling in some patients. Activating mutations in KRAS occur in ~40% of colorectal cancers and are thought to confer resistance to these drugs by bypassing the need for upstream EGFR signals. Activating mutations in BRAF – the direct downstream effector of KRAS – occur in ~10% of colorectal cancers and also probably confer resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies. Emerging evidence supports an additional role of oncogenic aberrations in the PI3K pathway in cetuximab and panitumumab resistance.