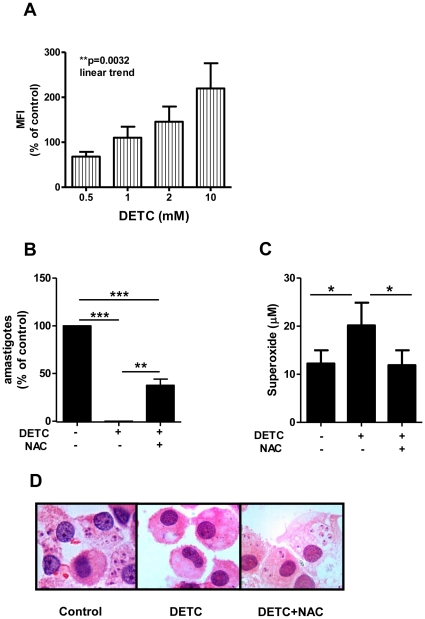
Figure 2. DETC leishmanicidal activity in human macrophages is reverted by antioxidant treatment.
(A) Uninfected PBMC from normal donors were triggered with PMA (100 ng/ml), treated with increasing doses of DETC and stained with hydroethidine for 30 minutes. Superoxide production was measured by flow cytometry (Mean Fluorescence Intensity - MFI). Monocytes were gated from the whole PBMC population based on size and granularity and analysed separately for superoxide production. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of 3 donors. (Repeated Measures ANOVA, *p = 0.018; post-test for linear trend, **p<0.0032). (B, C, and D) Leishmania amazonensis-infected human macrophages were treated with SOD inhibitor DETC (2 mM) in the absence or presence of antioxidant NAC (10 mM). (B) Hydroxylamine (0.5 mM) was added to the cultures and supernatant was collected at 48 h. Superoxide production was quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of 3 donors (Repeated Measures ANOVA, ***p = 0.0001; Bonferroni's correction, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01). (C) Cells were harvested at 48 h and the number of intracellular amastigotes was quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of 3 donors (Repeated Measures ANOVA, *p = 0.011; Bonferroni's correction, *p<0.05). (D) Cells were fixed on glass slides, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and photographed (1000× magnification).