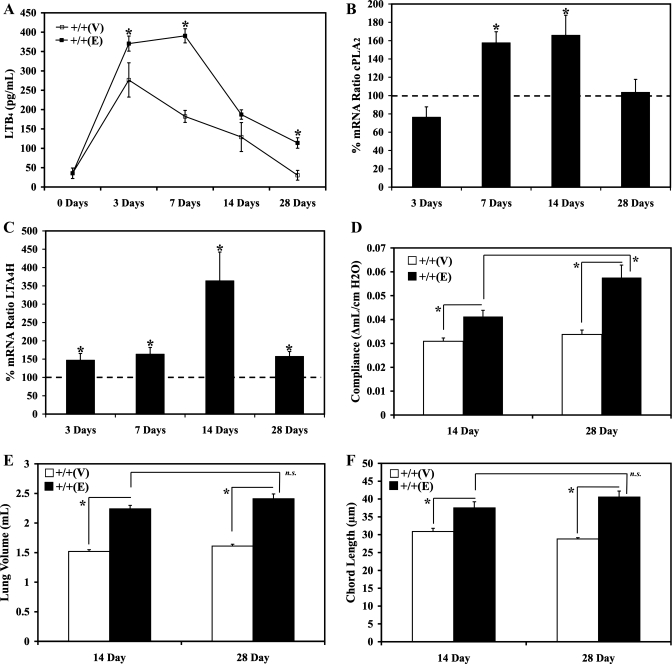
Fig. 2.
All wild-type 129J mice were exposed to either PBS vehicle or 0.75 μg elastase per kg mouse weight via an intranasal route. A: whole lung bronchoalveolar lavage fluid LTB4 0, 3, 7, 14, and 28 days after elastase exposure was assessed by an enzyme immunoassay. B: gene transcribing for cPLA2 was assessed by Sybergreen real-time RT-PCR 3, 7, 14, and 28 days after elastase exposure, normalized by GAPDH, expressed as % of target gene expression compared with the matched wild-type controls, and assessed for significance from the expected baseline (100%). C: genes transcribing for LTA4H were assessed by Sybergreen real-time RT-PCR 3, 7, 14, and 28 days after elastase exposure, normalized by GAPDH, expressed as % of target gene expression compared with the matched wild-type controls, and assessed for significance from the expected baseline (100%). D: premortem lung compliance was assessed with Flexivent 14 and 28 days after elastase exposure. E: postmortem whole lung volume was assessed by volume displacement technique after inflating the lungs at 25 cmH2O pressure melted 1% low-melting point agarose gel pressure. F: postmortem chord length was assessed in H&E-stained lungs after inflating the lungs with techniques described above. +/+, Wild type; V, vehicle; E, elastase. *P < 0.05; n.s., P value not significant.