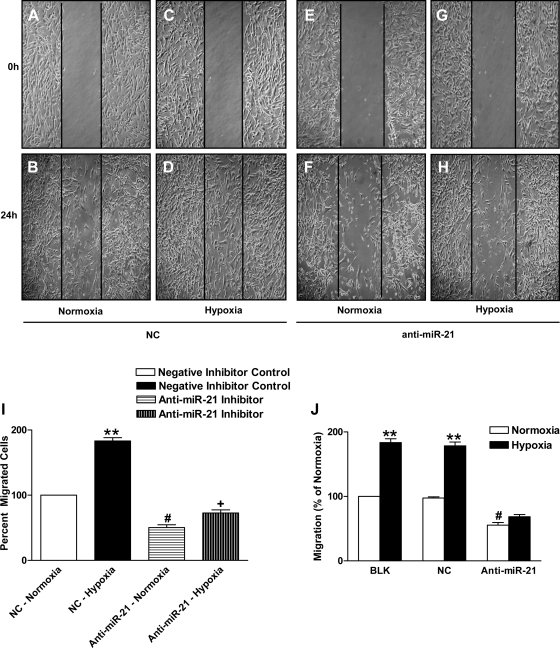
Fig. 3.
MiR-21 inhibition decreases HPASMC migration in hypoxia. A–H: miR-21 inhibition led to reduced HPASMC migration as measured by wound-healing migration assay. A–D represent the negative control group, and E–H represent the anti-miR-21 group. A, B, E, and F represent the normoxia group, and C, D, G, and H represent the hypoxia group. I: cell migration of negative inhibitor control HPASMCs after 24-h hypoxia increased by 83%. **P < 0.005 vs. control group. Cells with anti-miR-21 showed a 49% decrease in migration in normoxia compared with NC; #P < 0.05 vs. NC normoxic group. Hypoxia increased migration by only 22% in the anti-miR-21-treated cells; +P < 0.05 compared with cell migration in normoxia. J: HPASMC migration (percentage of normoxia) assayed using the Boyden chamber method showed increase in cell migration in hypoxia; **P < 0.005 vs. normoxia BLK and NC group. MiR-21 inhibition reduced SMC migration in normoxia, #P < 0.05, different from BLK and NC normoxia groups. Hypoxia did not increase migration in miR-21-inhibited cells significantly. Data are shown as means ± SE (n = 3).