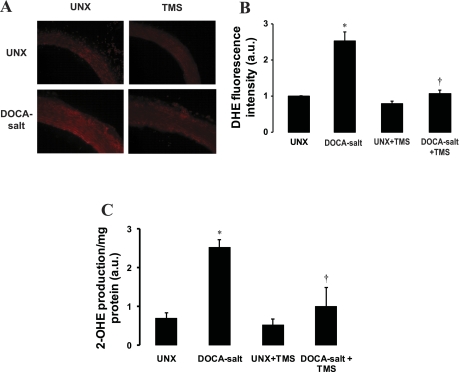
Fig. 5.
TMS prevents the increase in DOCA-salt-induced vascular superoxide production. The effect of TMS on vascular superoxide production was determined in transverse sections of thoracic aorta from animals in each of the different treatment groups. A: representative fluorescent photomicrographs of sections determined by dihydroethidium (DHE) fluorescent staining (materials and methods). B: quantification of fluorescence. Fluorescence was detected using a 585-nm filter on an Olympus inverted system microscope. Images were photographed using an Olympus digital camera, and quantification of fluorescence was determined using ImageJ 1.42. Mean fluorescence intensities were normalized to values for UNX control rats and are expressed in arbitrary units (a.u.). C: vascular superoxide production measured by monitoring the conversion of DHE to 2-hydroxyethidium (2-OHE) using HPLC (materials and methods). Data are means ± SE (n = 3–5). *P < 0.05, UNX vs. DOCA-salt. †P < 0.05, DOCA-salt vs. DOCA-salt + TMS.