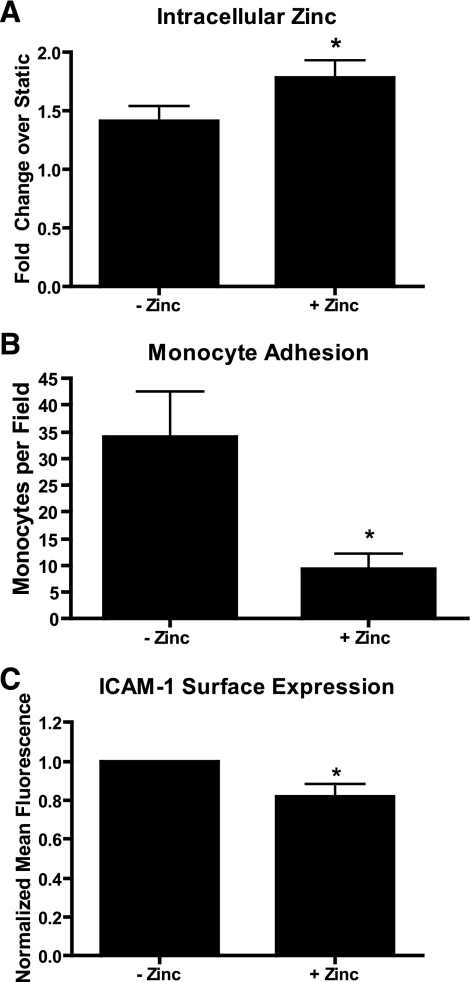
Fig. 4.
Addition of extracellular zinc inhibits the effects of reversing shear stress. Cells were exposed to reversing shear stress in regular media or media supplemented 50 μM ZnSO4 (n = 5; *P < 0.05). Cells shear stressed in zinc supplemented media had significantly increased levels of free zinc (A), reduced monocyte adhesion (B), and reduced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) surface expression (C).