Fig. 1.
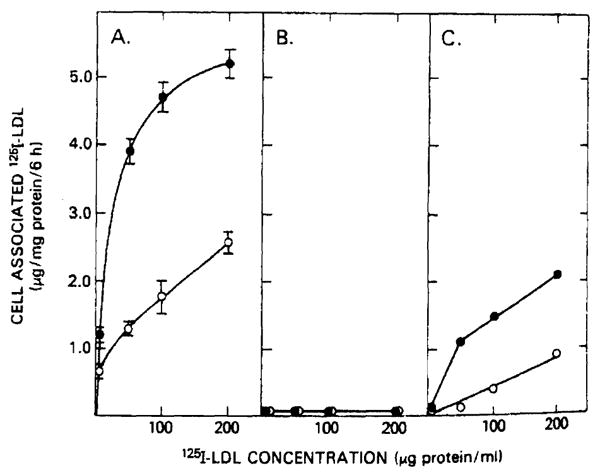
125I-labeled LDL binding and internalization by fibroblasts from normal and homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia patients. 5–7·105 fibroblasts per 2 cm2 well were incubated for 48 h in serum-free medium (●) or for 24 h in serum-free medium with 200 μg LDL protein/ml (○). After a 6-h, 37°C incubation with the indicated concentrations of 125I-labeled LDL, cells were washed six times with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.0). Protein and radioactivity determinations were performed on cells solubilized with 1 N NaOH. Values represent specifically bound and internalized 125I-labeled LDL defined as the difference in binding observed in the absence and presence of 10-fold excess of unlabeled LDL. Normal fibroblasts (panel A) and fibroblasts from patient 1 (panel B) and patient 2 (panel C) were evaluated.
