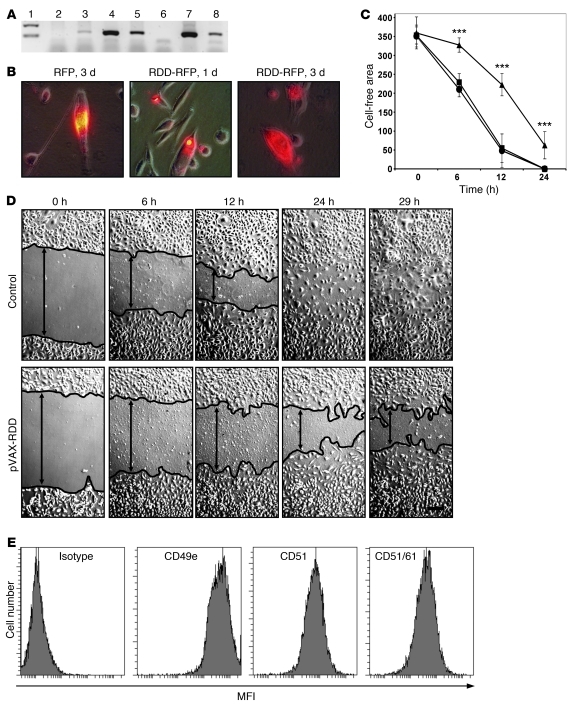
Figure 1. Expression and functional activity of RDD fusion proteins in vitro.
(A) Human fibroblasts transfected with different constructs were analyzed for RDD expression by RT-PCR (lanes: 1, weight marker; 2, untransfected fibroblasts; 3, transfected with pVAX-mock; 4, transfected with pVAX-RDD; 5, transfected with pVAX-RFP-RDD; 6, negative control; 7, plasmid pVAX-RDD [positive control 1]; 8, plasmid pVAX-RFP-RDD [positive control 2]. (B) Murine LL/2 cells were transfected with the pVAX-RFP-RDD or the pVAX-RFP plasmid as indicated. Protein expression was detected by fluorescence microscopy. Original magnification, ×400. (C) HUVEC cultures were scratched in a standardized fashion (wounding of the monolayer), thus creating a cell-free lane (width, 0.5 mm) in each culture. Cultures were then incubated with supernatant from untransfected human fibroblasts (circles), from human fibroblasts transfected with the pVAX-mock plasmid (squares), or the pVAX-RDD plasmid (triangles). Migration of cells into the cell-free lane was monitored. Each data point represents the mean of 10 measurements (± SD). Units on the y-axis: μm. ***P < 0.001. (D) Representative HUVEC cultures described in C. The controls shown here are cultures incubated with supernatant from pVAX-mock–transfected fibroblasts, which were similar to the other controls. The margins of the cell layers are indicated by black lines. Original magnification, ×100. (E) Expression of the RDD target proteins, integrins αVβ3 and α5β1, on HUVEC as detected by flow cytometry. Strong signals are detected with antibodies directed against CD49e (α5 integrin subunit), CD51 (αV integrin subunit), and a combinatorial epitope of CD51 and CD61 (the αVβ3 integrin heterodimer).