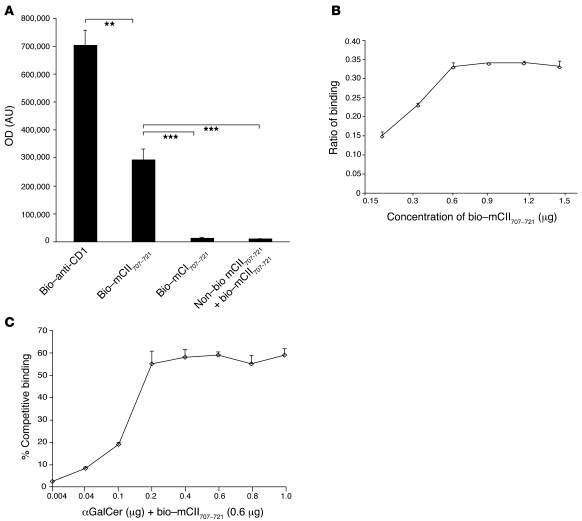
Figure 2. mCII707–721 binds CD1d.
(A) The binding capacity of mCII707–721 to CD1d was determined using ELISA plates coated with CD1d-Ig dimer, with biotin-labeled anti-CD1d (bio–anti-CD1) (positive control), biotin-labeled mCII707–721 peptide, or biotin-labeled mCI707–721 (negative control). Excess nonlabeled mCII707–721 peptide with biotin-labeled mCII707–721 peptide was used for competitive binding. Significant differences were seen in wells with biotin-labeled mCII707–721 peptide compared with negative control or excess nonlabeled peptide. (B) mCII707–721 binding to CD1d was concentration dependent, with a maximum binding capacity of 0.6 μg/ml. Ratio of binding is the fluorometer OD of the sample divided by the positive control OD. (C) αGalCer and biotinylated-labeled mCII707–721 peptide compete for binding to CD1d. Biotinylated-labeled mCII707–721 peptide binding to CD1d is considered as 100% binding. Data are mean ± SD, n = 3–4. **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.