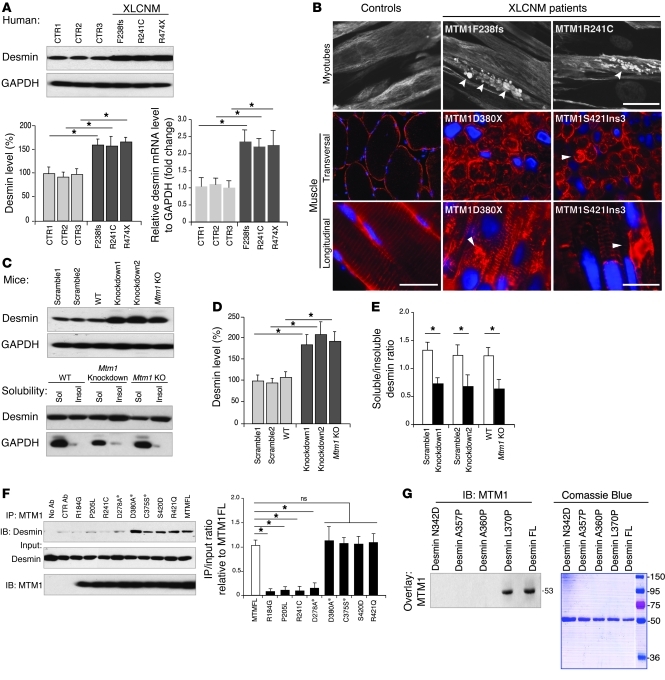
Figure 3. Effect of MTM1 depletion and mutation on desmin expression and localization.
(A) Desmin was overexpressed in an XLCNM patient’s myoblast (R474X, F238 frameshift, and R241C mutations) compared with controls (CTR1–CTR3); corresponding histograms show desmin protein and mRNA levels over 3 independent experiments (*P ≤ 0.05). (B) Desmin aggregation in XLCNM patient myotubes and muscle biopsies. XLCNM mutations are denoted; arrowheads indicate desmin aggregates. Scale bars: 50 μm. (C) Effect of Mtm1-KD (in C2C12) or -KO background (primary myoblasts from Mtm1-KO muscle) on desmin expression and solubility. (D and E) Quantification of C. (F) Effect of WT and XLCNM-linked or artificial (asterisks) MTM1 mutations on desmin interaction. Histograms show that several XLCNM mutations located in the interacting domain interfered with desmin binding. Quantification of the level of immunoprecipitated desmin/input relative to control (MTM1-FL) was correlated from 3 independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.05. (G) Effect of DRM-linked desmin mutations on MTM1 binding. Far-Western blot of recombinant WT and mutated desmin using recombinant MTM1 protein for overlay suggested that MTM1 only bound to DES-L370P and WT desmin. Lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous (white line).