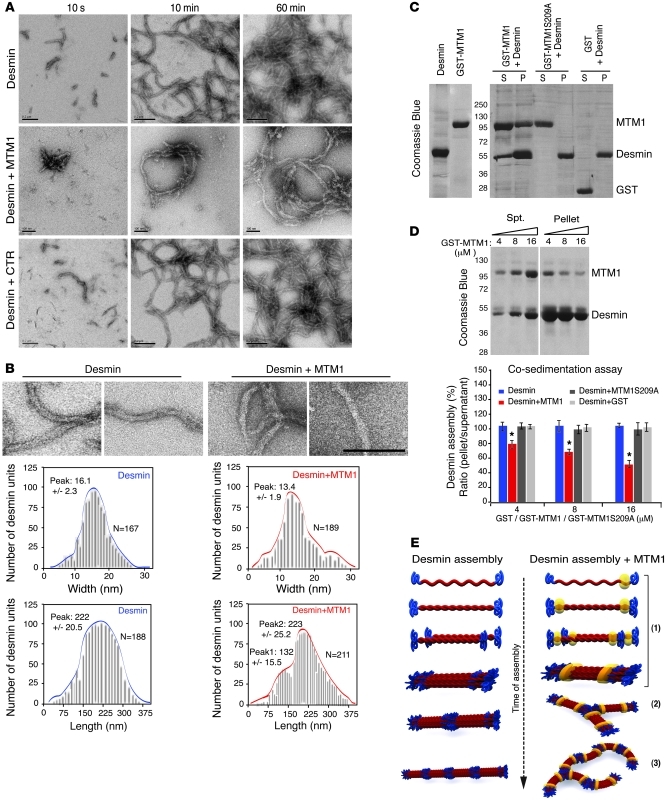
Figure 5. Effect of MTM1 on desmin filament polymerization.
(A) Effect of MTM1 on in vitro assembly of desmin filaments. Assembly of recombinant desmin alone (scale bars: 200 nm) or in the presence of MTM1 WT (scale bars: 100 nm) or the control protein Sumo (scale bars: 200 nm) was monitored by electron microscopy at the indicated times. Addition of WT MTM1 led to irregular and ribbon-like filaments. (B) Filament parameters (width and length at 5 minutes of assembly) in the presence or absence of MTM1. Scale bar: 200 nm. (C) MTM1 cosedimented with desmin and interfered with polymerization. SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue showed desmin exclusively in the pellet fraction (P; polymerized) in the presence of GST or GST-MTM1S209A, while it was also present in the soluble fraction (S; unpolymerized) in the presence of GST-MTM1. (D) Increasing amounts of recombinant GST-MTM1 caused a decrease in desmin polymerization. Lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous (white line). Quantification of desmin assembly (calculated as the ratio of band intensities in pellet/supernatant) in the presence of increasing amounts (4, 8, and 16 μM) of GST-MTM1, GST-MTM1S209A, or GST. Data were correlated from 2 independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.05. (E) Model of MTM1’s effect on desmin assembly in vitro. In phase 1 of desmin assembly, 8 tetrameric subunits, made from 2 antiparallel, half-staggered coiled-coil dimers, associate laterally to form ULFs after initiation of assembly. In phase 2, ULFs and short filaments longitudinally anneal to other ULFs. In phase 3, filaments evolve to radial compacted structures. MTM1 addition (yellow) interferes with filament assembly in vitro, leading to a branched-like phenotype at the squiggles step and a ribbon-like structure.