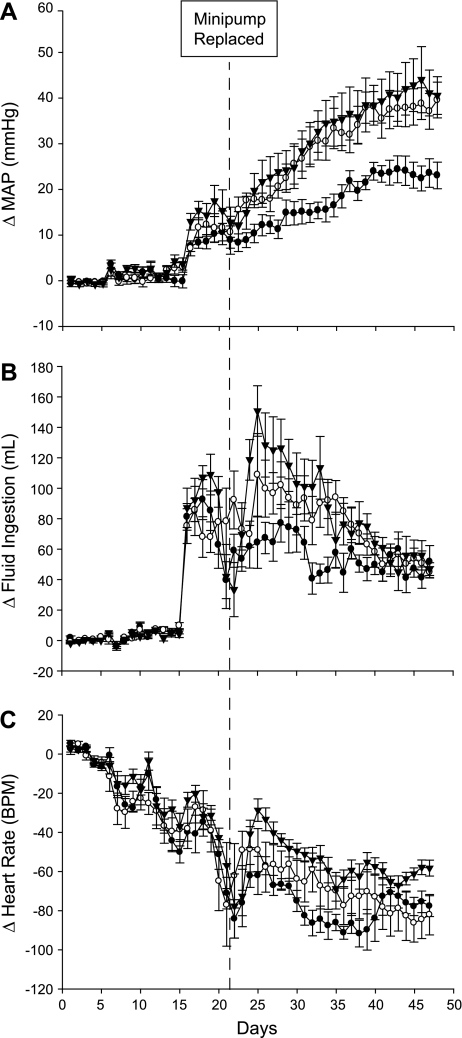
Fig. 5.
Effect of early cessation of benzamil treatment. Shown are 24-h means for MAP (A), fluid ingestion (B), and HR (C) for Vehicle-DOCA (n = 7, ○, animals from protocol 1), Benzamil-DOCA (n = 7, ●, animals from protocol 1), and Benzamil-Stop (n = 7, ▴, animals from protocol 2) rats. The day of the minipump replacement surgery, when Benzamil-Stop rats ceased benzamil treatment, is noted by a dotted line. P < 0.05 for all effects noted. A: 24-h averages for MAP. Benzamil-Stop rats showed identical pressure profiles to Vehicle-DOCA rats, and were significantly different from Benzamil-DOCA rats. B: while fluid ingestion initially matched between the 2 benzamil groups, when Benzamil-Stop animals stopped receiving benzamil treatment, their fluid ingestion rapidly rose to match that of the Vehicle-DOCA rats, with no significant differences observed between Vehicle-DOCA and Benzamil-Stop rats. C: all treatment groups showed similar HR decreases with no significant between group differences observed. All 3 groups showed a significant decrease in HR over the course of the study.