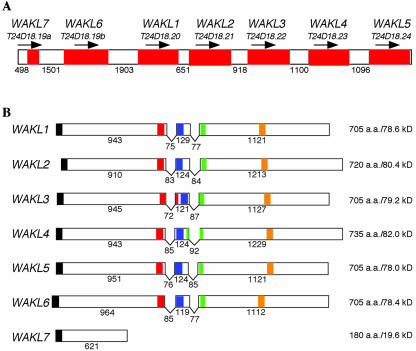
Figure 1.
Genomic organization of the WAKL gene cluster. A, Cartoon of the region of chromosome 1 containing the WAKL cluster. The identities of each gene (red shaded boxes) and the corresponding BAC gene from which it was derived are given above. The arrow above each gene corresponds to the direction in which it is transcribed. The unshaded areas correspond to the intergenic regions. The lengths of each intergenic region are given in the number of nucleotide base pairs between the stop codon of the preceding gene and the predicted start codon of the gene that follows. B, Cartoon of each of the WAKL genes. The identity of each gene is indicated at the left. Exons are shown as boxes. The “V” between each exon indicates the introns. Regions of each sequence displaying similarity with predicted functional domains are indicated with shaded boxes as follows: N-terminal signal sequence (black), EGF2-like domain (red), calcium-bind EGF domain (blue), transmembrane domain (green), and Ser/Thr protein kinase active site (orange). The numbers under each exon and intron correspond to their respective lengths in nucleotide base pairs. The size and molecular mass (excluding the signal peptide) for each of the predicted proteins are shown at the right.