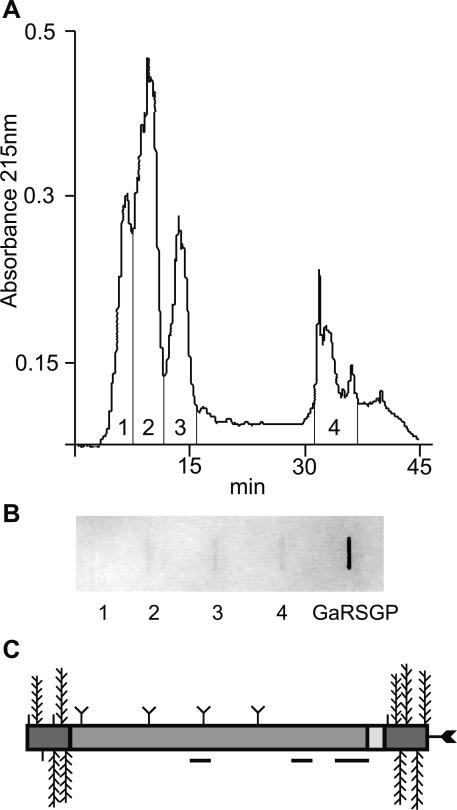
Figure 3.
Separation of AGPs and FLAs by RP-HPLC and detection of N-glycans using wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). A, Separation of β-glucosyl Yariv precipitated proteoglycans into four fractions by RP-HPLC. B, Slot blot representing approximately 40 μg of total carbohydrate from four fractions of proteoglycans and 250 μg of a control, galactose-rich stylar glycoprotein (Sommer-Knudsen et al., 1996), a known N-linked glycoprotein from Nicotiana alata, were detected for their ability to bind WGA. Fractions two to four and galactose-rich stylar glycoprotein bind to WGA, indicating the presence of N-glycans. C, Schematic representation of the predicted structure of native FLA7 after processing and posttranslational modifications. Horizontal lines below the protein backbone represent peptides sequenced from a trypsin digest of fraction four (Tables I and II). Posttranslational modifications include Pro residues hydroxylated to Hyp and O-linked sugars added to these Hyp residues (vertical lines, arabinooligosaccharides; feathers, type II AG polysaccharide chains) in the AGP regions (dark gray). Predicted N-glycosylation sites in the fasciclin domain (medium gray) are indicated by a Y shape and a C-terminal GPI anchor by an arrow.