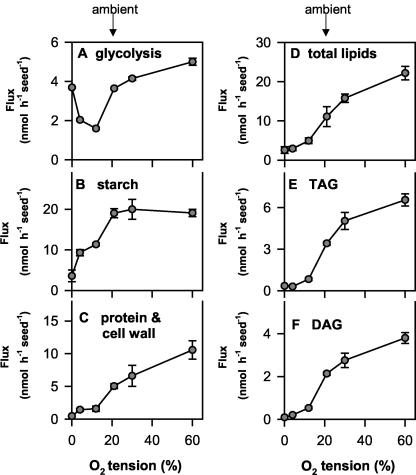
Figure 5.
Oxygen affects metabolic fluxes in developing seeds. The specific activity of the hexose phosphate pool (see below) and label incorporation into the relevant fractions (see Fig. 4) was used to calculate absolute rates of metabolic fluxes in seeds. The specific activity of the hexose phosphate pool was calculated by dividing the label retained in phosphoesters (Fig. 4B) by the total carbon of the phosphoester pool (see Fig. 7). The obtained values were divided by 2 to get the mean specific activities during the 2-h labeling period: 29 ± 9, 43 ± 8, 72 ± 5, 54 ± 18, 35 ± 12, and 44 ± 4 dpm nmol-1 at 0%, 4%, 12%, 21%, 30%, and 60% (v/v) O2, respectively. A, Glycolytic flux (the sum of the flux to the organic acids and amino acids); B, the rate of starch synthesis; C, flux into structural components (cell wall plus protein); D, rate of total lipid synthesis; E, rate of TAG synthesis; F, rate of DAG synthesis. The results are means ± se (n = 4-5 separate siliques from different plants). Error bars are not shown when they are smaller than the symbol.