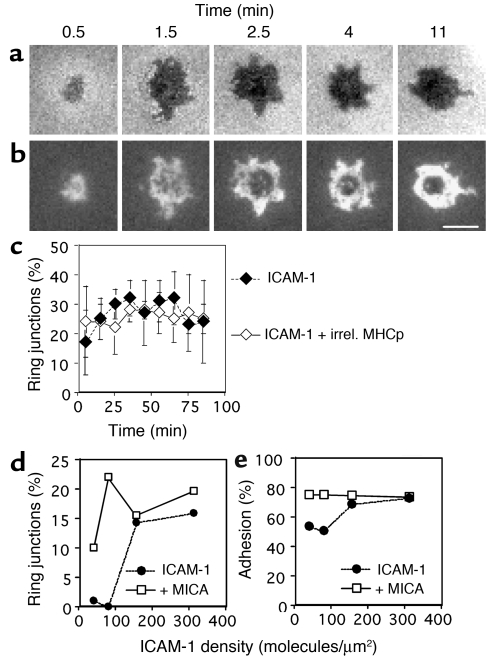
Figure 2.
The kinetics of and the irrelevant MHCp complex and ICAM-1 density dependence of ring junction and contact formation by CTL clones. (a and b) A CER43 cell on a bilayer containing 200 molecules/μm2 Cy3-ICAM-1–GPI alone. (a) Interference reflection microscopy images showing contact development (darker areas represent closer contact). (b) Fluorescence images showing LFA-1–ICAM-1 interaction during ring junction development. Cy3–ICAM-1 in grayscale (white represents the highest ICAM-1 density). The mean duration of transient ring junctions is 15 minutes, and a cell can make one to four ring junctions within an hour, with intervening migration. Scale bar: 5 μm. (c) Effect of irrelevant (irrel.) MHCp complexes on ring junction formation. The kinetics of ring junction formation were assessed for populations of CER43 cells on 200 molecules/μm2 Cy3–ICAM-1–GPI (filled diamonds) or 40 molecules/μm2 irrelevant Alexa 488-HLA-A2–IV9 (open diamonds). Ring junction formation reached a steady state within 15 minutes. No significant difference was detected without or with irrelevant MHCp complexes. (d) Percentage of ring junction formation by CTL clone 68A62 as a function of ICAM-1 density in the absence (filled circles) and presence (open squares) of 100 nM MICA on bilayers containing 50% Ni2+/NTA lipids. (e) Percentage of adhering 68A62 CTL clone cells as a function of ICAM-1 density in the absence (filled circles) and presence (open squares) of 100 nM MICA on bilayers containing 50% Ni2+/NTA lipids. Data in d and e are representative of data for 68A62 and CER43 CTL clones. In each case, over 1,000 cell contacts were analyzed to generate the graphs.