Abstract
The title compound, C14H11NO3, was isolated from the roots of Clausena wallichii. The carbazole ring system is approximately planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.039 Å) and the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 4.63 (7)°. An intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond generates an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal, molecules are linked into a zigzag network extending parallel to the ac plane by O—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For compounds isolated from plants of genera Rutaceae and their pharmacological activity, see: Ito et al. (1997 ▶); Kongkathip & Kongkathip (2009 ▶); Laphookhieo et al. (2009 ▶); Li et al. (1991 ▶); Maneerat & Laphookhieo (2010 ▶); Maneerat et al. (2010 ▶); Sripisut & Laphookhieo (2010 ▶); Tangyuenyongwatthana et al. (1992 ▶); Yenjai et al. 2000 ▶). For a related structure, see: Fun et al. (2009 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For the stability of the temperature controller used in the data collection, see Cosier & Glazer, (1986 ▶).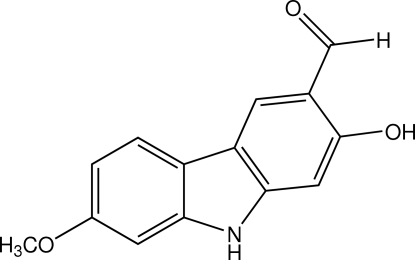
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H11NO3
M r = 241.24
Orthorhombic,
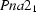
a = 12.4352 (4) Å
b = 17.6564 (5) Å
c = 5.0839 (1) Å
V = 1116.23 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.84 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.23 × 0.19 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.831, T max = 0.918
25207 measured reflections
2026 independent reflections
2018 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.030
wR(F 2) = 0.097
S = 1.31
2026 reflections
170 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.64 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.63 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 851 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.17 (19)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810033805/ci5167sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810033805/ci5167Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1O1⋯O2 | 0.81 | 1.96 | 2.6453 (17) | 143 |
| O1—H1O1⋯N1i | 0.81 | 2.53 | 3.0457 (15) | 123 |
| N1—H1N1⋯O2ii | 0.85 (2) | 2.10 (2) | 2.941 (2) | 172 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 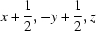 ; (ii)
; (ii) 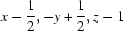 .
.
Acknowledgments
SL and WM are grateful to the Thailand Research Fund through the Royal Golden Jubilee PhD Program (grant No. PHD/0006/2552) and Mae Fah Luang University for financial support. SC thanks Prince of Songkla University for generous support through the Crystal Materials Research Unit. The authors also thank Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Research University Grant (No. 1001/PFIZIK/811160).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Rutaceae plants are known to be rich sources of coumarins and carbazole alkaloids. Many of them have been isolated from several genera of Rutaceae especially from Clausena genus (Laphookhieo et al., 2009; Maneerat et al., 2010; Sripisut & Laphookhieo 2010; Kongkathip & Kongkathip 2009; Ito et al., 1997; Li et al., 1991; Tangyuenyongwatthana et al., 1992) and some of these compounds show interesting pharmacological activities (Maneerat & Laphookhieo 2010; Yenjai et al. 2000). Although Clausena wallichii is one of the Rutaceae plants, however phytochemical reports on the chemical constituents from this plant are rare. As part of our continuing study of chemical constituents and bioactive compounds from Thai medicinal plants, we report herein the crystal structure of the title compound, which was isolated from the roots of C. wallichii collected from Phrae province in the northern region of Thailand.
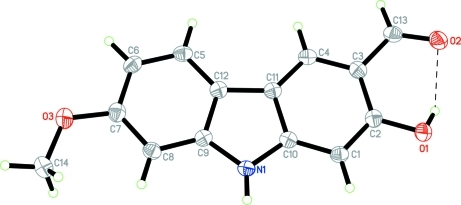
The non-hydrogen atoms of the title molecule (Fig. 1) are almost coplanar. The carbazole ring system (C1-C12/N1) is planar with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.039 Å [maximum deviation 0.072 (1) Å for atom C7]. The pyrrole ring makes dihedral angle of 1.66 (7) and 3.12 (8)°, respectively, with the C1–C4/C10–C11 and C5–C9/C12 benzene rings. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings being 4.63 (7)°. The cabaldehyde and methoxy substituents at atoms C3 and C7, respectively, are coplanar with the benzene ring, as indicated by torsion angles C2–C3–C13–O2 = 0.0 (2)° and C14–O3–C7–C8 = 4.0 (2)°. An intramolecular O1—H1O1···O2 hydrogen bond (Table 1) generates an S(6) ring motif (Fig. 1 and Table 1) (Bernstein et al., 1995). The bond distances are within normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987) and comparable to a related structure (Fun et al., 2009).
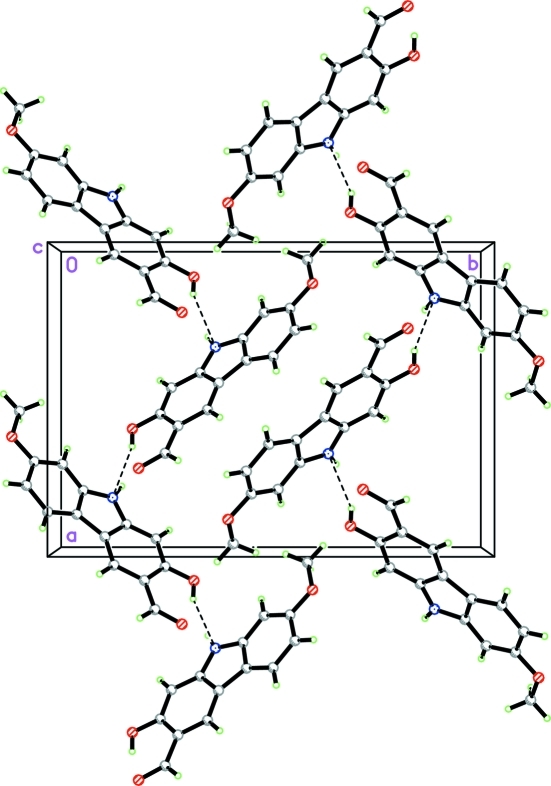
The crystal packing of the title compound is stabilized by intermolecular O—H···N and N—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) which link the molecules into a zigzag network extending parallel to the ac plane.
Experimental
The roots of C. wallichii (1.02 Kg) were successively extracted with CH2Cl2 over the period of 3 days each at room temperature to provide the crude CH2Cl2 extract which subjected to quick column chromatography (QCC) over silica gel eluted with a gradient of hexane-EtOAc (100% hexane to 100% EtOAc) to provide nine fractions (A-I). Fraction G (3.12 g) was further separated by QCC with a gradient of 10% EtOAc-hexane to 100% EtOAc to give seven subfractions (G1-G7). Subfraction G4 (118.9 mg) was subjected to repeated column chromatography using 30% EtOAc-hexane to yield the yellow solid of the title compound (12.8 mg). Yellow plate-shaped single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray structure determination were recrystallized from CH2Cl2/acetone (1:1 v/v) by the slow evaporation of the solvent at room temperature after several days; m.p. 496.7-498.8 K (decomposition).
Refinement
Atom H1N1 was located in a difference map and refined isotropically. The remaining H atoms were placed in calculated positions with O–H = 0.81, C–H = 0.93 for aromatic and CH, and 0.96 Å for CH3 atoms. The Uiso values were constrained to be 1.5Ueq of the carrier atom for methyl H atoms and 1.2Ueq for the remaining H atoms. A rotating group model was used for the methyl groups. The highest residual electron density peak is located at 1.81 Å from C9 and the deepest hole is located at 1.29 Å from C3. 851 Friedel pairs were used to determine the absolute structure.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme. The O—H···O hydrogen bond is shown as a dashed line.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the c axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C14H11NO3 | Dx = 1.435 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 241.24 | Melting point = 496.7–498.8 K |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2n | Cell parameters from 2026 reflections |
| a = 12.4352 (4) Å | θ = 4.4–69.9° |
| b = 17.6564 (5) Å | µ = 0.84 mm−1 |
| c = 5.0839 (1) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 1116.23 (5) Å3 | Plate, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.23 × 0.19 × 0.10 mm |
| F(000) = 504 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2026 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 2018 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 69.9°, θmin = 4.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.831, Tmax = 0.918 | k = −21→21 |
| 25207 measured reflections | l = −5→6 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0656P)2 + 0.054P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.097 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.31 | Δρmax = 0.64 e Å−3 |
| 2026 reflections | Δρmin = −0.63 e Å−3 |
| 170 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction coefficient: 0.053 (3) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 851 Friedel pairs |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Flack parameter: 0.17 (19) |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.59667 (8) | 0.17861 (6) | 0.4400 (2) | 0.0264 (3) | |
| H1O1 | 0.6537 | 0.1796 | 0.5149 | 0.056 (7)* | |
| O2 | 0.72058 (8) | 0.20104 (6) | 0.8557 (3) | 0.0294 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.12071 (9) | 0.59553 (6) | 0.5822 (3) | 0.0325 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.32559 (9) | 0.37021 (7) | 0.3111 (3) | 0.0203 (3) | |
| H1N1 | 0.2898 (14) | 0.3514 (10) | 0.185 (5) | 0.029 (5)* | |
| C1 | 0.46098 (10) | 0.26763 (8) | 0.3568 (3) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.4366 | 0.2391 | 0.2150 | 0.026* | |
| C2 | 0.54764 (10) | 0.24453 (8) | 0.5070 (3) | 0.0212 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.58509 (11) | 0.28796 (8) | 0.7249 (3) | 0.0220 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.53291 (10) | 0.35607 (8) | 0.7921 (3) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| H4A | 0.5569 | 0.3847 | 0.9339 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 0.36091 (11) | 0.50464 (7) | 0.8333 (3) | 0.0226 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.4092 | 0.5117 | 0.9708 | 0.027* | |
| C6 | 0.27613 (11) | 0.55440 (8) | 0.7967 (3) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.2680 | 0.5955 | 0.9094 | 0.029* | |
| C7 | 0.20217 (11) | 0.54348 (8) | 0.5906 (3) | 0.0238 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.21259 (10) | 0.48413 (7) | 0.4134 (3) | 0.0222 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.1644 | 0.4774 | 0.2756 | 0.027* | |
| C9 | 0.29943 (10) | 0.43496 (7) | 0.4528 (3) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.41167 (10) | 0.33567 (7) | 0.4277 (3) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.44591 (10) | 0.37986 (8) | 0.6456 (3) | 0.0194 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.37263 (11) | 0.44372 (8) | 0.6603 (3) | 0.0203 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.67188 (10) | 0.26163 (8) | 0.8877 (3) | 0.0244 (3) | |
| H13A | 0.6930 | 0.2923 | 1.0273 | 0.029* | |
| C14 | 0.03861 (12) | 0.58496 (9) | 0.3899 (4) | 0.0354 (4) | |
| H14A | −0.0179 | 0.6211 | 0.4184 | 0.053* | |
| H14B | 0.0101 | 0.5346 | 0.4043 | 0.053* | |
| H14C | 0.0684 | 0.5921 | 0.2174 | 0.053* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0261 (5) | 0.0281 (5) | 0.0251 (6) | 0.0080 (4) | −0.0009 (4) | −0.0024 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0282 (5) | 0.0358 (6) | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0098 (4) | −0.0016 (4) | 0.0011 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0291 (6) | 0.0340 (7) | 0.0104 (4) | −0.0052 (5) | −0.0053 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0207 (6) | 0.0215 (6) | 0.0187 (6) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0025 (5) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0224 (6) | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0188 (8) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0003 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0202 (6) | 0.0226 (6) | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0047 (5) | 0.0017 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0206 (7) | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0212 (8) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0207 (6) | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0183 (8) | −0.0035 (5) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0257 (7) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0199 (7) | −0.0044 (5) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0000 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0204 (6) | 0.0217 (8) | −0.0017 (5) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0028 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0246 (8) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0029 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0216 (9) | −0.0004 (5) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0195 (6) | 0.0191 (8) | −0.0028 (5) | 0.0020 (5) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0217 (7) | 0.0193 (8) | −0.0026 (4) | 0.0014 (5) | 0.0020 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0211 (6) | 0.0191 (6) | 0.0180 (8) | −0.0036 (5) | 0.0023 (5) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0214 (7) | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0206 (8) | −0.0030 (5) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0031 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0238 (6) | 0.0297 (7) | 0.0198 (9) | −0.0003 (5) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0025 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0353 (8) | 0.0360 (9) | 0.0348 (11) | 0.0131 (6) | −0.0077 (7) | −0.0022 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C2 | 1.3574 (17) | C5—C6 | 1.3850 (19) |
| O1—H1O1 | 0.81 | C5—C12 | 1.397 (2) |
| O2—C13 | 1.2401 (17) | C5—H5A | 0.93 |
| O3—C7 | 1.3685 (16) | C6—C7 | 1.407 (2) |
| O3—C14 | 1.426 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.93 |
| N1—C10 | 1.3671 (18) | C7—C8 | 1.388 (2) |
| N1—C9 | 1.3899 (18) | C8—C9 | 1.4000 (17) |
| N1—H1N1 | 0.85 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.93 |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (2) | C9—C12 | 1.402 (2) |
| C1—C10 | 1.3960 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.420 (2) |
| C1—H1A | 0.93 | C11—C12 | 1.4517 (18) |
| C2—C3 | 1.425 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.93 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4086 (19) | C14—H14A | 0.96 |
| C3—C13 | 1.438 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.96 |
| C4—C11 | 1.379 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.96 |
| C4—H4A | 0.93 | ||
| C2—O1—H1O1 | 104.9 | C8—C7—C6 | 121.71 (13) |
| C7—O3—C14 | 117.62 (13) | C7—C8—C9 | 116.58 (13) |
| C10—N1—C9 | 109.00 (13) | C7—C8—H8A | 121.7 |
| C10—N1—H1N1 | 124.3 (12) | C9—C8—H8A | 121.7 |
| C9—N1—H1N1 | 126.2 (12) | N1—C9—C8 | 128.06 (14) |
| C2—C1—C10 | 116.99 (14) | N1—C9—C12 | 109.20 (12) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 121.5 | C8—C9—C12 | 122.69 (13) |
| C10—C1—H1A | 121.5 | N1—C10—C1 | 128.02 (14) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 117.68 (14) | N1—C10—C11 | 109.13 (12) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 120.64 (13) | C1—C10—C11 | 122.84 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.67 (13) | C4—C11—C10 | 119.28 (13) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.83 (13) | C4—C11—C12 | 134.53 (14) |
| C4—C3—C13 | 118.83 (14) | C10—C11—C12 | 106.18 (12) |
| C2—C3—C13 | 121.25 (13) | C5—C12—C9 | 119.41 (12) |
| C11—C4—C3 | 119.36 (14) | C5—C12—C11 | 134.10 (14) |
| C11—C4—H4A | 120.3 | C9—C12—C11 | 106.45 (12) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.3 | O2—C13—C3 | 124.75 (14) |
| C6—C5—C12 | 118.88 (14) | O2—C13—H13A | 117.6 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.6 | C3—C13—H13A | 117.6 |
| C12—C5—H5A | 120.6 | O3—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.71 (14) | O3—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 119.6 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 119.6 | O3—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—C8 | 123.77 (14) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—C6 | 114.52 (14) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C10—C1—C2—O1 | −179.79 (13) | C2—C1—C10—N1 | 179.92 (13) |
| C10—C1—C2—C3 | 0.13 (19) | C2—C1—C10—C11 | −1.0 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.74 (12) | C3—C4—C11—C10 | −0.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (2) | C3—C4—C11—C12 | 177.97 (14) |
| O1—C2—C3—C13 | −3.2 (2) | N1—C10—C11—C4 | −179.38 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C13 | 176.88 (12) | C1—C10—C11—C4 | 1.4 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C11 | 0.0 (2) | N1—C10—C11—C12 | 1.49 (15) |
| C13—C3—C4—C11 | −176.59 (13) | C1—C10—C11—C12 | −177.74 (12) |
| C12—C5—C6—C7 | 0.7 (2) | C6—C5—C12—C9 | 0.8 (2) |
| C14—O3—C7—C8 | 4.0 (2) | C6—C5—C12—C11 | −176.30 (14) |
| C14—O3—C7—C6 | −175.73 (14) | N1—C9—C12—C5 | −178.86 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7—O3 | 178.13 (13) | C8—C9—C12—C5 | −1.4 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −1.7 (2) | N1—C9—C12—C11 | −1.06 (15) |
| O3—C7—C8—C9 | −178.74 (13) | C8—C9—C12—C11 | 176.40 (12) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 1.0 (2) | C4—C11—C12—C5 | −1.9 (3) |
| C10—N1—C9—C8 | −175.26 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C5 | 177.08 (15) |
| C10—N1—C9—C12 | 2.04 (15) | C4—C11—C12—C9 | −179.18 (15) |
| C7—C8—C9—N1 | 177.45 (14) | C10—C11—C12—C9 | −0.25 (15) |
| C7—C8—C9—C12 | 0.49 (19) | C4—C3—C13—O2 | 176.58 (13) |
| C9—N1—C10—C1 | 176.99 (13) | C2—C3—C13—O2 | 0.0 (2) |
| C9—N1—C10—C11 | −2.19 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1O1···O2 | 0.81 | 1.96 | 2.6453 (17) | 143 |
| O1—H1O1···N1i | 0.81 | 2.53 | 3.0457 (15) | 123 |
| N1—H1N1···O2ii | 0.85 (2) | 2.10 (2) | 2.941 (2) | 172 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI5167).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst.19, 105–107.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Fun, H.-K., Maneerat, W., Laphookhieo, S. & Chantrapromma, S. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2497–o2498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ito, C., Katsuno, S., Ohta, H., Omura, M., Kajirua, I. & Furukawa, H. (1997). Chem. Pharm. Bull 45, 48–52.
- Kongkathip, N. & Kongkathip, B. (2009). Heterocycles, 79, 121–144.
- Laphookhieo, S., Sripisut, T., Prawat, U. & Karalai, C. (2009). Heterocycles, 78, 2115–2119.
- Li, W. S., McChesney, J. D. & El-Feraly, F. S. (1991). Phytochemistry 30, 343–346.
- Maneerat, W. & Laphookhieo, S. (2010). Heterocycles 81, 1261–1269.
- Maneerat, W., Prawat, U., Saewan, N. & Laphookhieo, S. (2010). J. Braz. Chem. Soc 21, 665–668.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sripisut, T. & Laphookhieo, S. (2010). J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res 12, 612–617. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tangyuenyongwatthana, P., Pummangura, S. & Thanyavuthi, D. (1992). Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol 14, 157–162.
- Yenjai, C., Sripontan, S., Sriprajun, P., Kittakoop, P., Jintasirikul, A., Tanticharoen, M. & Thebtaranonth, Y. (2000). Planta Med 66, 277–279. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810033805/ci5167sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810033805/ci5167Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report