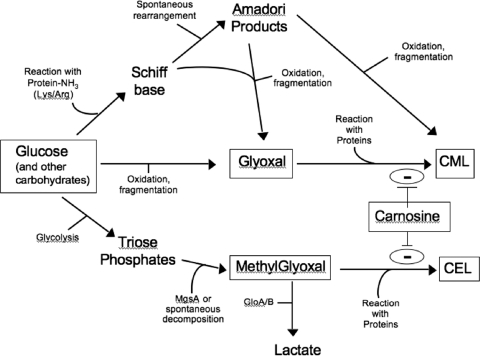
FIG. 6.
Proposed model of carnosine protection against glycation. Carnosine most likely interacts with reactive carbonyl intermediate compounds (e.g., glyoxal and methylglyoxal) to inhibit the formation of advanced glycated end products (e.g., CML and carboxyethyl lysine). Other mechanisms of protection are also probable (see text for details). Abbreviations: MgsA, methylglyoxal synthase; CML, carboxymethyl lysine; CEL, carboxyethyl lysine. GloA and GloB are glyoxylase enzymes I and II, respectively.