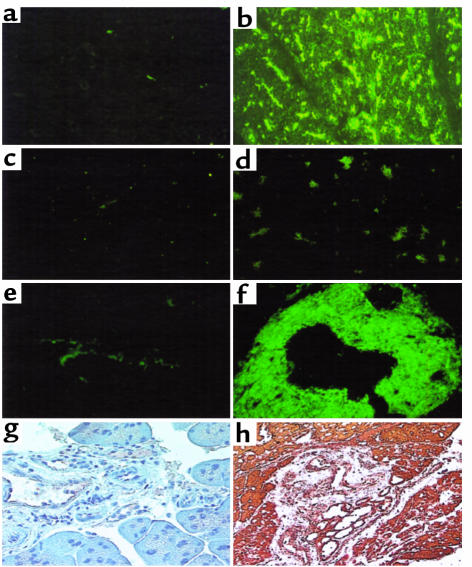
Figure 5.
Autoantibodies in serum of pS2-dnRII transgenic mice before cerulein treatment. IgG-type autoantibodies are identified by indirect immunofluorescence using monkey pancreatic sections and an FITC-coupled rat anti-mouse immunoglobulin polyclonal antibody. (a) The absence of autoantibody in the sera of wild-type littermates is shown. (b) The presence of antipancreatic acinar cell antibodies in the serum of pS2-dnRII mice is shown. Positive sera containing IgG-autoantibodies showed blurry, droplike staining in pancreatic acinar cells. When the sera from pS2-dnRII transgenic mice were reacted with proteins extracted from the pancreata of pS2-dnRII mice, the positive staining seen in b disappeared (d). Result of staining using sera from the wild-type mice reacted with protiens from the pancreata of wild-type mice is shown (c). IgA-type autoantibody against the pancreatic duct was noted in the sera of pS2-dnRII transgenic mice (f), whereas such antibody was absent in the sera of wild-type littermates (e). Expressions of SP3-1, an autoantigen of pancreatic ductal cells, were also markedly increased in the pancreatic duct of pS2-dnRII mice (h) compared with that of wild-type littermates (g).