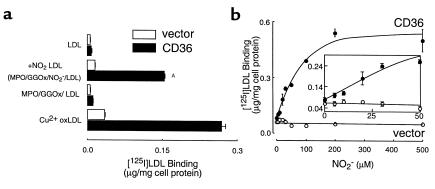
Figure 2.
Binding of [125I]LDL by CD36-transfected cells after modification by MPO-generated nitrating intermediates. (a) [125I]LDL was incubated with isolated human MPO (30 nM), glucose (100 μg/mL), glucose oxidase (20 ng/mL), and NO2– (0.5 mM) in sodium phosphate buffer supplemented with DTPA (100 μM) for 8 hours at 37°C (complete system, NO2-LDL) as described in Methods. Reactions were stopped by addition of BHT (40 μM) and catalase (300 nM), and then lipoproteins (5 μg/mL) were incubated with CD36- or vector-transfected 293 cells at 4°C for 3 hours in the appropriate media containing additional catalase (300 nM) and BHT (20 μM). LDL modified by dialysis against copper for 5 hours (Cu2+ oxLDL, 5 μg/mL) was used as a positive control. Cellular binding of lipoproteins was subsequently determined as described in Methods. AP < 0.001 for comparison versus LDL modified in the presence of MPO- and a H2O2-generating system (MPO/GGOx/LDL). (b and inset) [125I]LDL (0.2 mg/mL) was incubated with isolated human MPO (30 nM), glucose (100 μM), glucose oxidase (20 nM), and the indicated concentrations of NO2– in sodium phosphate buffer supplemented with DTPA (100 μM) and NaCl (100 mM) overnight at 37°C. Cellular binding of lipoproteins (10 μg/mL) was subsequently determined as described in Methods. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations of a representative experiment performed 3 times.