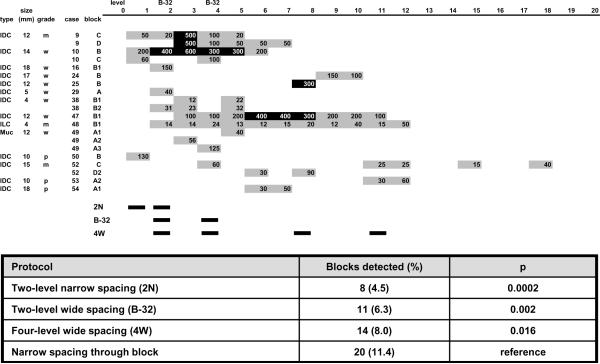
Figure 2. Location by level and size of occult metastases detected in sentinel lymph nodes.
A comprehensive sectioning strategy evaluating cytokeratin immunohistochemical stains every 0.18 mm entirely through the paraffin block was used. Occult metastasis detection rates for two-level narrow spacing (2N), two-level wide spacing (B-32), and four-level wide spacing (4W) protocols were compared to the reference comprehensive multilevel narrow spacing protocol. The comprehensive protocol is statistically significantly different from the remaining sampling protocols. Note that the smallest p-value and lowest rate of metastasis detection is associated with the 2N protocol sampling the most superficial levels of the paraffin block indicating the two-level narrow spacing protocol is the least effective at detecting occult micrometastases. Gray boxes indicate occult metastases no larger than 0.2 mm (isolated tumor cell clusters; ITCs) and black boxes indicate occult metastases larger than 0.2 mm (micrometastases). Each box contains the size in μm (microns) of the largest occult metastasis identified on the level. Blocks 10B and 47B1 contained contiguous micrometastases present on several levels with non-contiguous ITCs on sections superficial and deep to the micrometastasis.