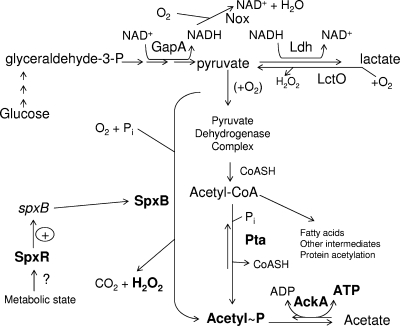
FIG. 1.
Model of central metabolism in S. pneumoniae growing aerobically in glucose-containing BHI broth. An abbreviated version of the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas glycolytic pathway is shown; this pathway converts glucose to pyruvate and generates two ATP molecules. Pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase (Ldh), regenerating NAD+, and lactate can be converted back to pyruvate by lactate oxidase (LctO). NADH oxidase (Nox) also converts NADH back to NAD+. Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acetyl∼P (AcP) is formed from acetyl-CoA by Pta or from pyruvate by pyruvate oxidase (SpxB), which also produces H2O2. Transcription of the spxB gene is positively regulated by the SpxR CBS-HotDog domain regulator. Acetyl∼P is converted to acetate and another molecule of ATP by AckA. See the text for additional information and references.