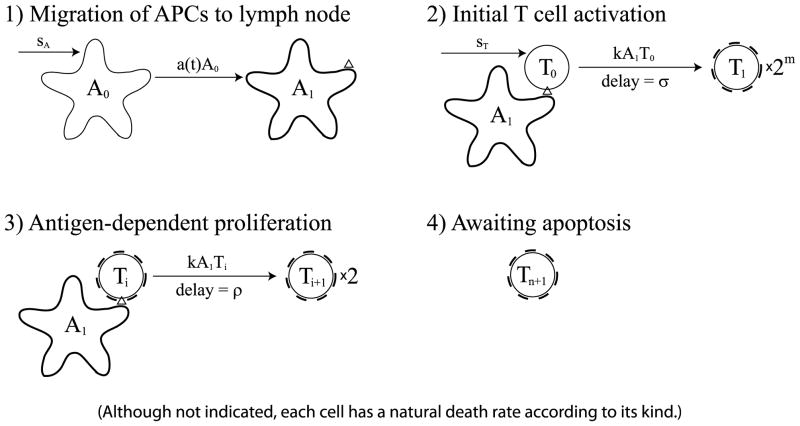
Fig. 1.
The cell division-based program. (1) Immature APCs pick up antigen at the site of infection at a time-dependent rate a(t). These APCs mature and migrate to the lymph node. (2) Mature antigen-bearing APCs present antigen to naïve T cells causing them to activate and enter the minimal developmental program of m divisions. (3) Activated T cells that have completed the minimal program continue to divide upon further interaction with mature APCs for up to n additional divisions. (4) T cells that have completed the maximal number of divisions stop dividing and wait for apoptosis. Although not indicated, each cell in the diagram has a natural death rate according to its kind.