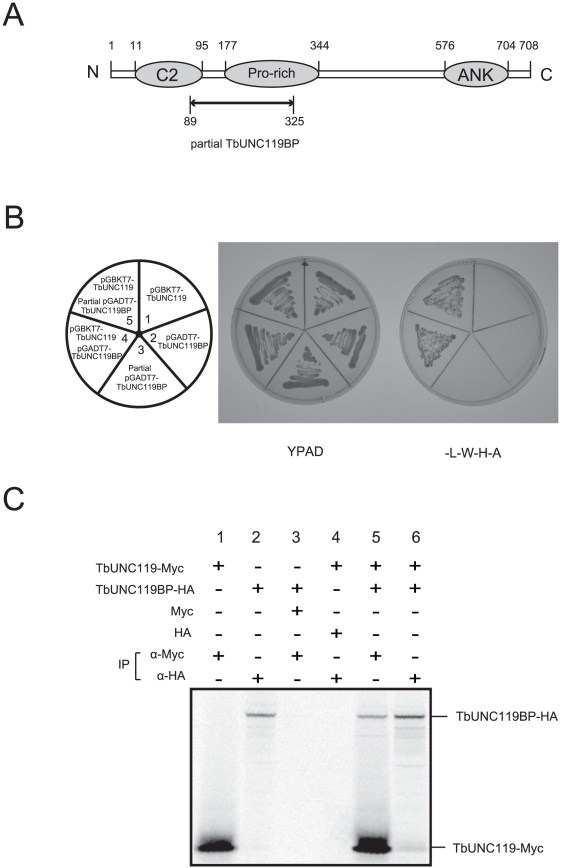
Figure 2. TbUNC119 interacted with TbUNC119BP (Tb927.7.5300).
A. Schematic representation of the molecular structure of TbUNC119BP. Numbers represent amino acid residues. C2, Pro (proline)-rich, and ANK (ankyrin) repeat motifs were found between residues 11 and 95, between residues 177 and 344, and between residues 576 and 704, respectively, in the TbUNC119BP molecule. Arrow indicates a region which was harbored in the prey plasmid (Fig. 2B). B. Yeast two-hybrid analysis of TbUNC119 interaction. Yeast strain AH109 was co-transformed with pGBKT7-TbUNC119 and pGADT7-TbUNC119BP (full-length or partial; Fig. 2A). Growth of transformants on media -L-W-H-A (without leucine, tryptophan, histidine, and adenine) indicates protein-protein interaction (sectors 4 and 5). Yeast cells transformed with each plasmid failed to grow on media -L-W-H-A (sectors 1, 2 and 3). C. Co-immunoprecipitation of TbUNC119 and TbUNC119BP. 35S-labeled Myc-tagged TbUNC119 and 35S-labeled HA-tagged TbUNC119BP were expressed in vitro using the TNT T7 Quick coupled transcription/translation system and 35S-methionine. Lysates were precipitated on anti-Myc agarose or anti-HA agarose. Immunoprecipitated samples were separated by electrophoresis.