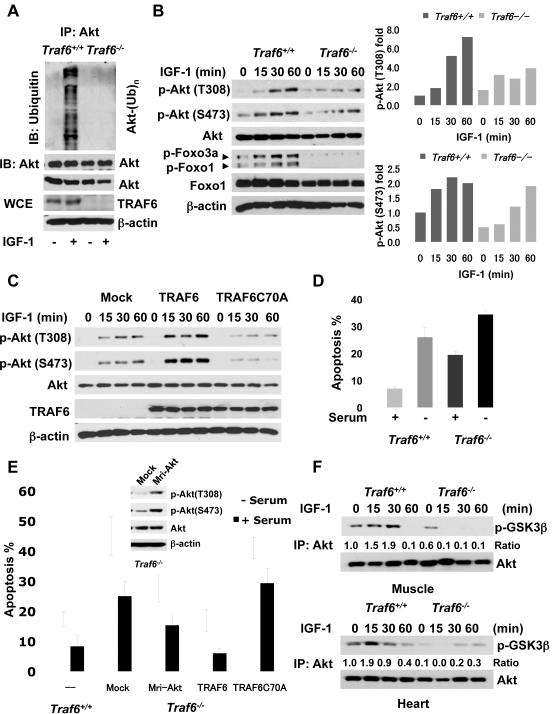
Fig. 2.
TRAF6 is required for ubiquitination and phosphorylation of Akt. (A) Traf6+/+ and Traf6−/− MEFs were serum-starved and were treated with or without IGF-1 for 30 min; WCE were collected for immunoprecipitation with Akt, followed by immunoblot analysis. (B) MEFs were serum-starved, treated with IGF-1 for various time points, and harvested for immunoblot analysis. The quantification results were shown on the right panel. (C) Primary Traf6−/− MEFs infected with Mock, TRAF6, or TRAF6 C70A mutant were treated with IGF-1 at various time points and harvested for immunoblot analysis. (D) MEFs were cultured in 10% FBS or serum-starved for 2 days, and apoptosis was determined by Annexin V staining, followed by flow cytometry analysis. Results are presented as mean values ±standard deviation (S.D.) (E) Primary MEFs were infected with Mock, constitutively active Akt (Mri-Akt), TRAF6, or TRAF6 C70A and apoptosis and immuno blot analysis were determined. Results are presented as mean values ± S.D. (F) Heart and skeletal muscle isolated from WT and Traf6−/− mice (n=4) injected with IGF-1 at various time points was subjected to an in vitro Akt kinase assay and immunoblot analysis.