Figure 5. Increasing internal Na+ concentration increases resting Na+ −K+ ATPase activity in all cell types.
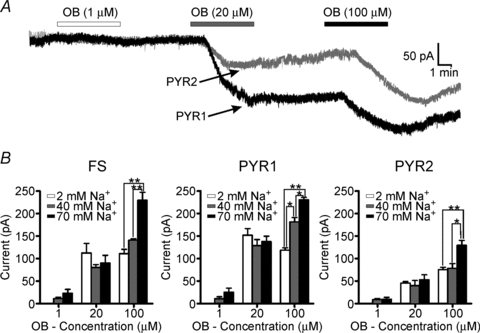
A, voltage clamp trace from a PYR1 (black) or PYR2 (grey) neuron loaded with 70 mm Na+ internally through the patch pipette. After sufficient time was allowed for dialysis of the Na+ (> 10 min) and stability achieved in the baseline recording, ouabain (OB) was applied at various concentrations (1, 20 and 100 μm). Application of 20 μm ouabain produced two distinct groups of responses in PYR neurons, consistent with our previous findings in non-loaded neurons, and was used for PYR neuron grouping (PYR1 and PYR2). B, mean (±s.e.m.) current recorded from FS (n = 18), PYR1 (n = 10) or PYR2 (n = 14) neurons in different internal Na+ concentrations. Cells were loaded with control (2 mm), 40 or 70 mm Na+. Loading with 70 mm Na+ increased the current induced by 100 μm, but not lower concentrations of ouabain, in all cell types. Only PYR1 neurons were more sensitive to 40 mm Na+ compared to control (2 mm). *P > 0.05, **P > 0.01. Vm = −70mV.
