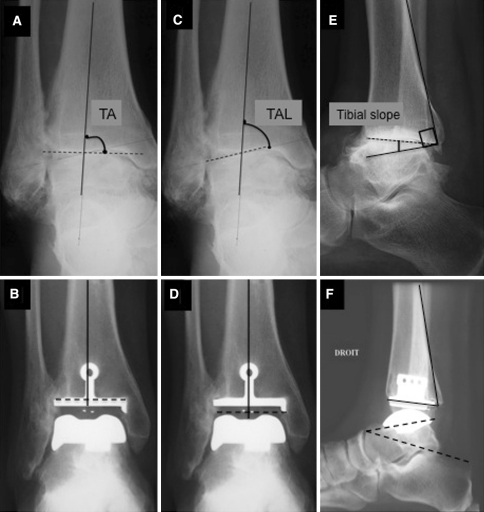
Fig. 1A–F.
Weightbearing AP and lateral radiographs of the ankle were performed. A representative example is shown. On the AP view, the tibial angle (TA) was measured between the axis of the tibia and the articular surface of the tibial plafond (A) before and (B) after surgery. The talar angle (TAL) was measured between the axis of the tibia and the superior articular surface of the talus (C) before and (D) after surgery. The tibial slope was measured on the lateral radiograph as the angle between a line drawn along the posterior tibial cortex and a second line connecting the most anterior and posterior points of the tibial joint surface (E) before and (F) after surgery. (F) The talocalcaneal angle was measured between the undersurface of the talar component and a reference line drawn from the superior border of the talonavicular joint and the most superior aspect of the posterior process of the calcaneus [1]. Any variation greater than 5° in these measurements was considered component migration.