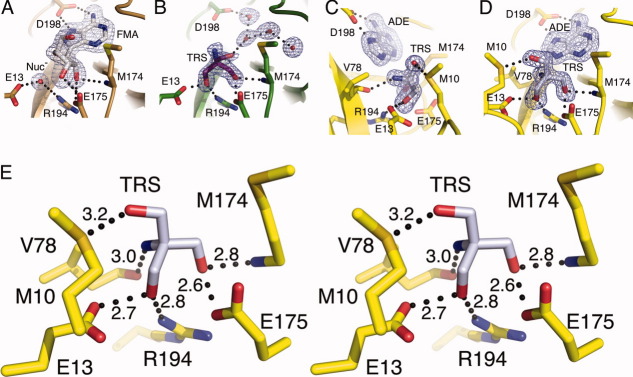
Figure 7.
The MTAN active site can accommodate a variety of hydrogen bonding patterns. Each of the three enzymes in the closed conformation clearly exhibit the orientation of the bound compounds in Fo–Fc omit maps contoured at 3σ. (A) Fo–Fc omit map of the FMA bound structure reflects characteristics seen in previous MTAN-FMA complexes. Both FMA and the nucleophilic water molecule (Nuc−) were omitted during map calculation. (B) The HpMTAN-TRS structure in the same orientation as (A) exhibits the Fo-Fc omit map where the tris molecule and four ordered water molecules within the adenine binding site were omitted from the map calculation. Note that the orientation of tris is such that the amine moiety is clearly pointed upward roughly along the Y-axis. (C) and (D) show the active site of the HpMTAN-ADE-TRS structure in two different orientations. Panel (D) is in the same orientation as (A) and (B) and shows the clear density for the three hydroxymethyl moieties. The orientation of tris in the active site is different from that observed in panel (B). Panel (C) is rotated roughly 90 degrees along the Y-axis to more clearly show the density for the amine moiety of tris. The Fo − Fc omit map was calculated while omitting both the tris and adenine molecules. (E) Stereo diagram of the HpMTAN-ADE-TRS active site showing the hydrogen bonding network with conserved residues of the active site. Dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonds and distances between donors and acceptors are shown in angstroms.