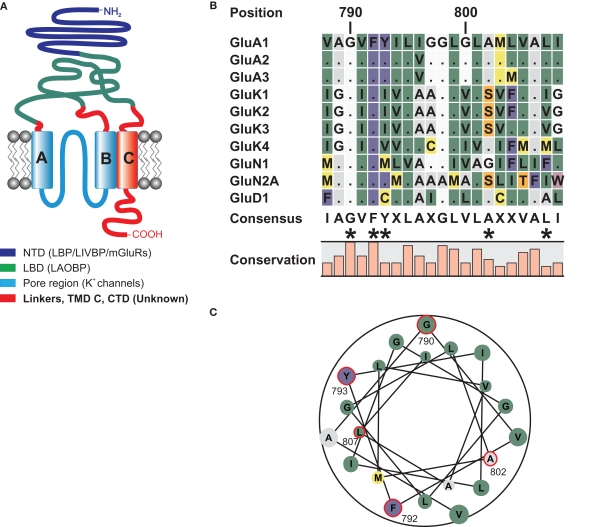
Figure 1.
(A) Domain topology of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Other proteins homologous to the domains are given in brackets. The NTD shares homologies with the bacterial leucine binding protein (LBP) and leucine–isoleucine–valine binding protein (LIVBP), as well as the LBD of metabotropic glutamate receptors (O'Hara et al., 1993). The LBD of iGluRs shares sequence similarities with the bacterial leucine–arginine–ornithine binding protein (LAOBP) (Kuryatov et al., 1994), and the pore region shows structural homology to the pore of potassium channels with an inverted orientation (Kuner et al., 2003). For the linker regions, the TMD C, and the CTD no homologous sequences have been identified. (B) Local sequence alignment of the TMD C regions of all iGluR subunits that were used as TMD C donors in domain transplantation constructs. Two residues, G790 and F792 are conserved among all 18 iGluR subunits. Residues that were altered in this study are indicated by asterisks. (C) Helical wheel representation of the TMD C of GluA1. Residues investigated in this study are encircled in red. Numbering refers to the mature GluA1 sequence, without the signal peptide.