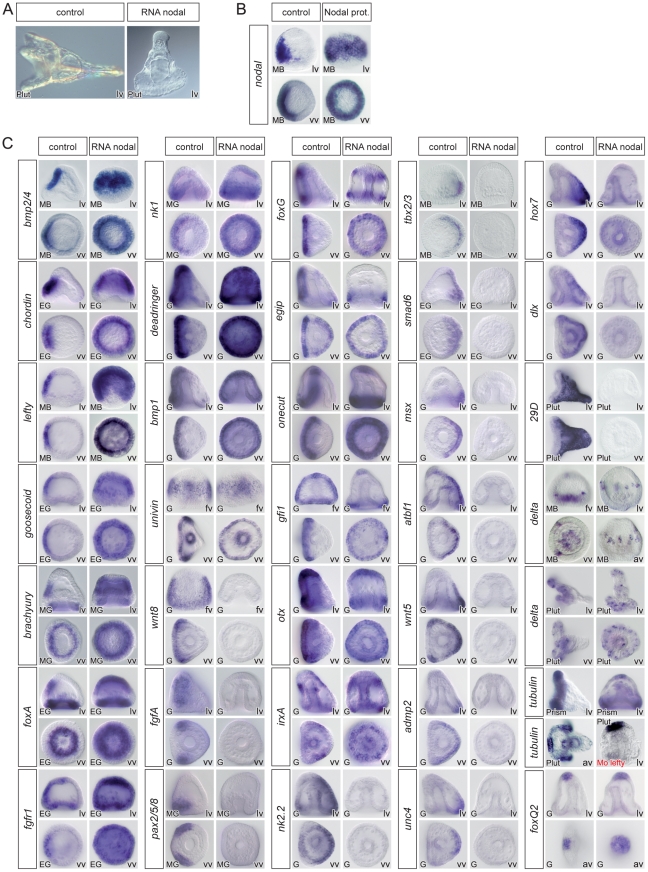
Figure 2. Overexpression of nodal represses the expression of ciliary band and dorsal marker genes and expands the expression of ventral markers genes.
(A) morphology of nodal overexpressing embryos at 72h. (B) treatment with recombinant Nodal protein induces ectopic expression of nodal in a large belt of ectodermal cells. (C) Injection of nodal mRNA (200–400 µg/ml) caused the expression of most ventral marker genes to become radial. In most cases, however, the animal pole domain appeared to be resistant to ectopic expression of nodal. Overexpression of nodal also radialized the expression of dri, bmp1 and univin, which are expressed in a broad domain encompassing the presumptive ventral ectoderm and ciliary band. In contrast, Nodal strongly antagonized the expression of ciliary band marker genes such as wnt8, fgfA, pax2/5/8, foxG, egip, onecut, gfi1, otx, tubulinß3 or Delta in the equatorial region. Nodal overexpression efficiently repressed the expression of all the genes expressed in the dorsal ectoderm but did not affect the expression of marker genes of the animal pole (tubulinß3, foxQ2, Delta). Note that, starting at gastrula stage, irxA is expressed in a patch of animal-ventral cells that likely corresponds to the upper part of the presumptive stomodeum. Therefore in nodal overexpressing embryos, this territory becomes radial and forms a belt of cells near the animal pole. Also note that while a ciliary band does form in the vegetal region of nodal overexpressing embryos, as shown by the expression of ciliary band genes around the blastopore, no ciliary band forms in the vegetal region of lefty morphants as indicated by the absence of tubulinß3 expression. In contrast, nodal overexpression does not affect the expression of animal pole marker genes such as foxQ2. lv, lateral view, vv, vegetal pole view, av, animal pole view, fv, frontal view.