Fig. 3.
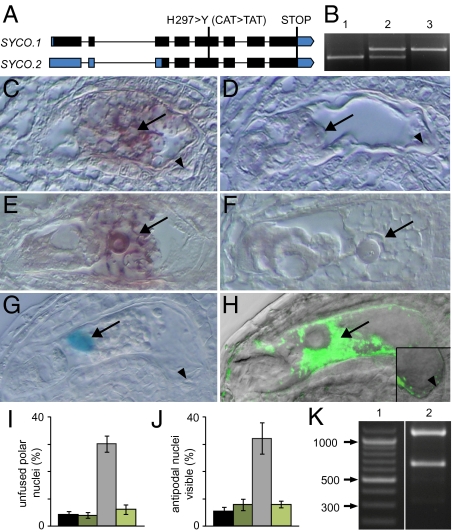
The cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase SYCO is expressed and required in the central cell but not in antipodals. (A) Gene structure of SYCO. Exons are depicted in bars, introns in lines. UTRs are indicated in blue, coding exons in black. The change in DNA and amino acid sequence in syco-1 is indicated. (B) PCR-based genotyping of the SYCO locus reveals that the genomic SYCO DNA driven by a 1.25-kb upstream promoter allows the generation of homozygous mutants. 1, SYCO/SYCO; 2, syco-1/SYCO; 3, syco-1/syco-1, pSYCO::SYCO/-. (C–F), In situ hybridization of SYCO mRNA in the female gametophyte before (C and D) and after (E and F) antipodal degeneration. (C and E) Antisense probe. (D and F) Sense probe. Arrow and arrowhead point at central cell and antipodals, respectively. (G) NLS_GUS expression driven by a 1.25-kb promoter fragment upstream of SYCO is restricted to the central cell nucleus (arrow). (H) Localization of pMEA::SYCO_GFP in the central cell (arrow) of the female gametophyte 2 d after emasculation (overlay of GFP fluorescence with differential interference contrast image). Inset: Magnification of the proximal end of the central cell and of the antipodals (arrowhead). (I and J) pMEA::SYCO_GFP complements the polar nuclei fusion (I) and antipodal PCD (J) defects in syco-1/SYCO plants. Black bar, wild type, n = 256; dark green bar, pMEA::SYCO_GFP, n = 355; gray bar, syco-1/SYCO, n = 342; light green bar, syco-1/SYCO, pMEA::SYCO_GFP, n = 426. Gametophytes were analyzed 2 d after emasculation. Error bars, mean ± SEM. (K) Digestion of PCR-amplified SYCO_GFP with BspMI discriminates between SYCO.1 and SYCO.2 cDNA. SYCO.1 is digested to 1,162 bp and 666 bp, SYCO.2 to 1,162 bp, 338 bp, and 332 bp. 1, ladder; 2, pMEA::SYCO_GFP.