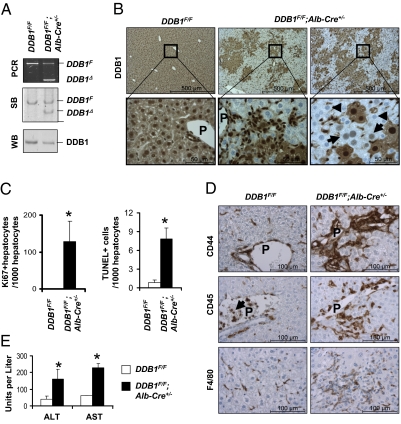
Fig. 3.
DDB1F/F;Alb-Cre+/− mice exhibited continuous hepatocyte turnover and chronic liver damage. (A) PCR and Southern blot (SB) analysis for DDB1F and DDB1Δ alleles in genomic DNA, and Western blot (WB) analysis of DDB1 protein levels from hepatocytes isolated from adult mice. (B) DDB1 IHC staining on liver sections from 6-wk-old mice. Arrows indicate hepatocytes freshly inactivated of the DDB1 gene, and arrowheads indicate hepatocytes completely depleted of DDB1 protein. (C) Quantification of Ki67-positive hepatocytes and TUNEL-positive cells on liver sections from three 6-wk-old mice. Values shown as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.01). (D) IHC staining for CD44, CD45, and F4/80. Abundant positive cells are found around portal areas. Arrows indicate CD45-positive blood cells in portal vein. (E) Measurement of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels. Values shown as means ± SEM; n = 3 (*P < 0.01).