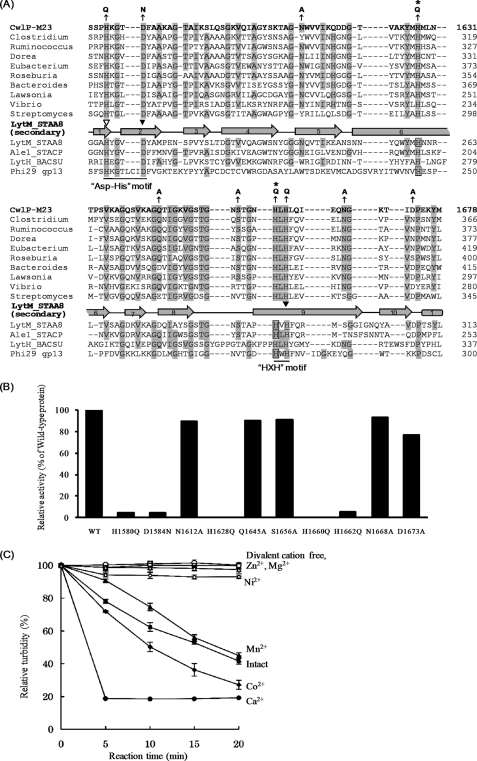
FIGURE 6.
Identification of the CwlP catalytic amino acid residues controlling dd-endopeptidase activity (digestion of linkage between d-Ala and A2pm) and the effect of divalent cations. A, alignment of the M23 domain of CwlP, homologous proteins, and Gly-Gly, l-Ala-d-Glu, and d-Ala-A2pm endopeptidases. The protein sequences were aligned using the ClustalW algorithm. The hydrolytic amino acid residues that are not related to the metal binding are denoted by boxes. Zinc binding sites in S. aureus LytM (28), Staphococcus capitis AleI (27), or φ29 Bacillus bacteriophage gp13 (31) are denoted by arrowheads (the open arrowhead shows the Zn2+ binding site for LytM and AleI, and the closed arrowheads represent Zn2+ binding sites for LytM, AleI, and gp13), respectively. Residues that are identical to CwlP are represented by shading, and the numbers represent amino acid positions starting from the N terminus of each protein. The gray rectangle and arrows represent α-helix and β-sheets, respectively, in S. aureus LytM (28). The HXH motif is the consensus one for Zn2+-metallopeptidases (28) and is conserved in all of the proteins shown here. However, the Asp-His motif described by Bochtler et al. (29) differs between gp13 and many other proteins (HX6D and HX3D, respectively) (where X is any letter). Arrows indicate amino acid residues that were mutated in this study. Asterisks denote the critical amino acid residues within CwlP-M23 that were identified in this study. Abbreviations: CwlP-M23, B. subtilis CwlP; Clostridium, Clostridium nexile protein; Ruminococcus, Ruminococcus lactaris protein; Dorea, Dorea formicigenerans protein; Eubacterium, Eubacterium ventriosum protein; Roseburia, Roseburia intestinalis protein; Bacteroides, Bacteroides capillosus protein; Lawsonia, Lawsonia intracellularis protein; Vibrio, Vibrio alginolyticus protein; Streptomyces, Streptomyces clavuligerus protein; LytM_STAA8, S. aureus LytM; Ale1_STACP, Staphylococcus capitis AleI; LytH_BACSU, B. subtilis LytH; Phi29 gp13, φ29 Bacillus bacteriophage gp13. S. aureus LytM and S. capitis AleI are Gly-Gly endopeptidases (4, 26). B. subtilis LytH is an l-Ala-d-Glu endopeptidase (5). φ29 Bacillus bacteriophage gp13 is a d-Ala-A2pm endopeptidase (31). B, in vitro cell wall hydrolytic activity. Purified cell walls (0.3 mg/ml) were digested with 0.15 μm (3 μg/ml) CwlP-M23 or the mutated CwlP-M23 for 30 min at 40 °C, pH 7.5. The reduction in turbidity of the solution was measured, and the decrease in turbidity with the mutated CwlP-M23 was compared with that of the wild-type, CwlP-M23. In this experiment, H1628Q and H1660Q exhibited no hydrolytic activity. C, hydrolytic activity of CwlP-M23 in the presence of divalent cations. After purified CwlP-M23 had been dialyzed against 25 mm EDTA and re-dialyzed against 50 mm MOPS-NaOH, pH 7.5, the turbidity of a cell wall solution (0.3 mg/ml) with 0.077 μm (1.5 μg/ml) CwlP-M23 and various divalent cations (1 mm) was measured (at 40 °C, pH 7.5). Closed squares, intact CwlP-M23 (without dialysis against EDTA); closed circles, Ca2+ ion; closed diamonds, Co2+ ion; closed triangles, Mn2+ ion; open squares, no cation; open circles, Zn2+ ion; open diamonds, Ni2+ ion; open triangles, Mg2+ ion. Error bars in C indicate the standard deviations for three independent experiments.