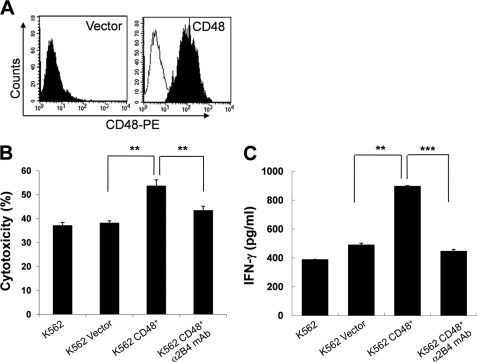
FIGURE 3.
CD48-expressing K562 target cells were more susceptible to NK cytotoxicity. A, K562 cells were transduced with pMFG retroviral vector carrying human CD48 cDNA, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” CD48 expression on empty vector-transduced or CD48-transduced K562 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. B, a standard 4-h 51Cr release assay was performed using NK cells cultured with 300 units/ml of IL-2 for 10–14 days as effector cells and parental K562 cells, empty vector-transduced K562 cells, or CD48-expressing K562 cells as targets. Where indicated, 5 μg/ml of anti-2B4 mAb was added during the 4-h cytotoxicity assay. Specific lysis (%), presented as mean ± S.D. of triplicates, at an E:T ratio of 10:1 was shown. The average NK cytotoxicity against K562, K562 vector, K562 CD48+, and K562 CD48+ with α2B4 mAb was 37.1 ± 1.2, 38.1 ± 0.9, 53.7 ± 2.5, and 43.3 ± 1.8%, respectively (**, p < 0.01). The data are representative of 5 independent experiments. C, LAK cells, cultured as described above, were incubated with parental, empty vector-transduced, or CD48-expressing K562 cells at an E:T ratio of 2:1 for 18 h. Where indicated, 5 μg/ml of anti-2B4 mAb was added during the assay. Secretion of IFN-γ into the supernatant was assessed by ELISA. The data are representatives of a minimum of 3 independent experiments. **, p < 0.01 and ***, p < 0.001, as determined by ANOVA combined with a Tukey post hoc test. Error bars represent S.D.