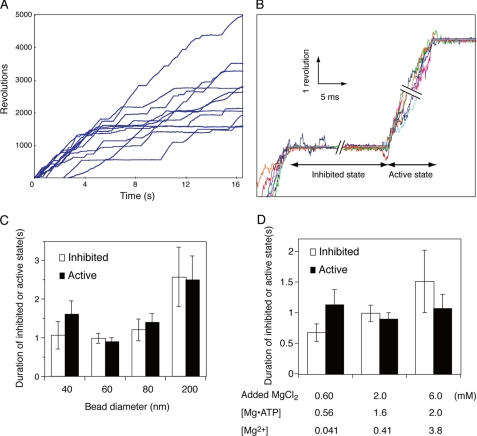
FIGURE 1.
High speed rotation of the γ subunit. A, time courses of γ subunit rotation under Vmax conditions. 60-nm diameter gold beads were attached to the γ subunit of F1 immobilized on a glass surface as described in Ref. 17 and under “Experimental Procedures.” ATP (2 mm) hydrolysis-dependent rotation was followed for 16 s at 24 °C. B, inhibited and active states of single molecule F1-ATPases. The time courses of eight beads in the active and inhibited states are superimposed. Individual beads are shown in different color traces. C, average duration of inhibited (open bars) and active (closed bars) states during rotation of different size beads. Beads were attached to the γ subunit of immobilized F1, and ATP-dependent rotation was followed as described above. Error bars represent S.E. D, effects of free Mg2+ on the duration of inhibited (open bars) and active (closed bars) states. 60-nm gold beads were attached to the γ subunit, and ATP-dependent rotation was followed in the presence of 2 mm ATP with 0.60, 2.0, or 6.0 mm total MgCl2. The free Mg2+ concentrations were calculated as described under “Experimental Procedures.”