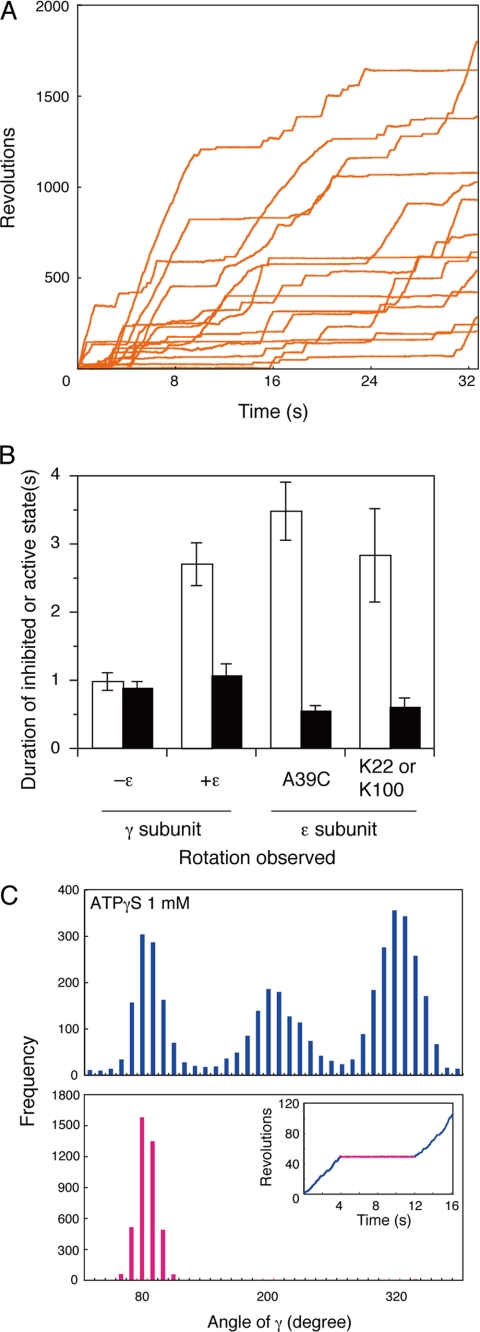
FIGURE 5.
Effects of the ϵ subunit on F1-ATPase rotation. A, time courses of γ subunit rotation in the presence of 100 nm ϵ subunit. ATP (2 mm)-dependent rotation in the presence of 100 nm ϵ subunit was followed for 32 s. B, effect of the ϵ subunit on the duration time of the inhibited (open bars) and active (closed bars) states. Gold beads were attached to the γ or ϵ subunit (via ϵA39C or primary amine-modified ϵLys-22/ϵLys-100), and rotation was followed for 32 s. The effects of the ϵ subunit on rotation are shown together with the controls lacking the ϵ subunit (−ϵ). The duration times for the inhibited and active states were recorded and are shown with S.E. C, angular distributions of the centroids of gold beads during rotation. Rotation of a gold bead was followed at 24 °C in the presence of 1.0 mm ATPγS (inset), and angular distributions of the centroid during the active state (blue) and the inhibited state (red) are graphed.