Figure 3. Immediate early gene expression (Egr-1) in vasopressin cells in the anterior olfactory nucleus following odour exposure.
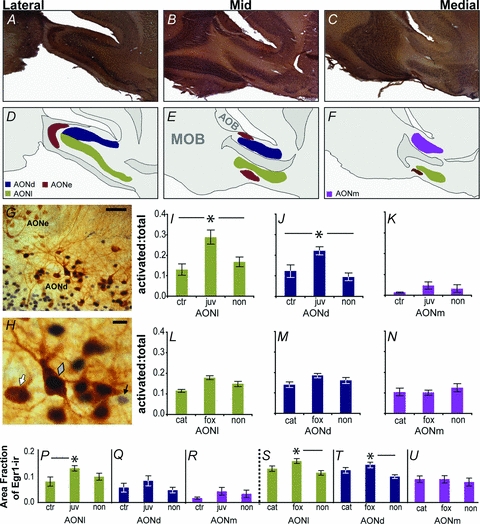
The AON is subdivided into the pars externa (AONe) and pars principalis. The pars principalis is composed of three subdivisions, the pars dorsalis (AONd), pars lateralis (AONl), and pars medialis (AONm) (A–C). Diagrammatic representations of the cellular layers of AON subdivisions are indicative of a typical adult male or female eGFP-vasopressin rat (D–F; MOB, main olfactory bulb; AOB, accessory olfactory bulb). Vasopressin cells were most regularly located along the superficial edge of the deep cellular layer of the pars principalis (G; scale bar = 50 μm). An eGFP-vasopressin+/Egr-1−(white arrow), a double labelled (grey diamond), and an eGFP-vasopressin−/Egr-1+ cell (black arrow) are shown (H; scale bar = 10 μm). Exposure to a conspecific juvenile increased the ratio of vasopressin cells expressing the Egr-1 protein over the total number of vasopressin cells (i.e. activated: total) in AONl (I) and AONd (J), but not AONm (K) as compared to both cage agitation (ctr) and non-social odour (non) controls. Exposure to heterospecific predator odours (cat, fox) did not alter the ratio of vasopressin cells expressing the Egr-1 protein over the total number of vasopressin cells as compared to non-social odour controls in AONl (L), AONd (M), or AONm (N). Exposure to a juvenile increases overall Egr-1 expression in the AONl (P), but not AONd (Q) or AONm (R). Exposure to fox odour increases Egr-1 expression in the AONl (S) and AONd (T), but not AONm (U), over non-social odour controls. Egr-1 expression was widespread in the AON, and is represented as the total area fraction covered by Egr-1 immunoreactivity within a sampled area within an AON subdivision. Asterisks denote significant differences in post hoc analyses.
