FIGURE 4. Auxiliary and accessory subunits of ionotropic glutamate receptors.
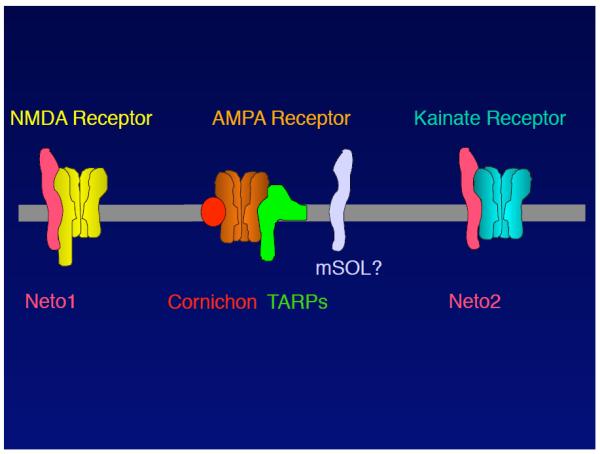
Ionotropic glutamate receptors are pharmacologically classified as AMPA-, NMDA-, and kainate-sensitive glutamate receptors. Several transmembrane subunits have been proposed to date, but remain unconfirmed. The NMDAR complex comprises Neto1, which is a CUB domain-containing protein. The AMPAR complex comprises TARPs and cornichon. Notably, it remains unclear whether AMPAR/TARP/cornichon form a tripartite complex. The C. elegans AMPAR complex comprises SOL-1, which is a CUB domain-containing protein. Therefore, mammalian AMPAR complexes may comprise a mammalian homolog of SOL-1 (mSOL). The kainate receptor complex comprises Neto2, which is a CUB domain-containing protein. The high sequence homology between Neto1 and 2 raises the question of whether Neto1 and 2 act as auxiliary subunits for both NMDA and kainate receptors.
