Table 2.
Relative rates of nicotinamidase enzymes for various nicotinamide analogues
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | BbNic | PfNic | Pnc1 | SpNic |
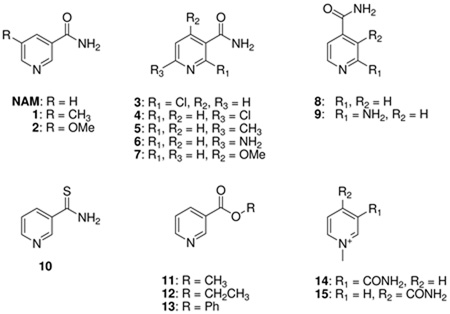
| NAM | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 1a | 0.51 | 3.30 | 0.80 | 1.63 |
| 2b | 2.21 | 6.46 | 2.06 | 1.37 |
| 3b | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4b | 0 | 0 | 0.17 | 0.018 |
| 5a | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0 | 0.11 |
| 6a | NDc | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.36 |
| 7b | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.050 | 0.065 |
| 8b | NDc | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9b | NDc | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0.44 | 0 |
| 11b | NDc | 65.0 | 0.15 | 0.035 |
| 12b | NDc | 0.023 | 0.044 | 0.0086 |
| 13b | NDc | 0.13 | 0.031 | 0.031 |
| 14b | NDc | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15b | NDc | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Reactions were run in 150 µL total volume containing 1 mM α-ketoglutarate, 250 µM NADPH, 3 units of GDH, and 500 µM of nicotinamide analogue in 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.3, for control experiments, reactions containing 500 µM of nicotinamide were run in parallel. Reactions were initiated by addition of nicotinamidase enzymes, decreasing of fluorescence intensity was monitored by a microplate reader.
Reactions were in 25 µL total volume containing 500 µM of nicotinamide analogue in 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.3, for control experiments, reactions containing 500 µM of nicotinamide were run in parallel. Reactions were initiated by addition of nicotinamidase enzymes, incubated 37 °C and quenched by addition of 10% trifluoroacetic acid. Reactions were quantified by integrating area of peaks corresponding to nicotinic acid analogue.
ND = Not determined. NAM: nicotinamide.
