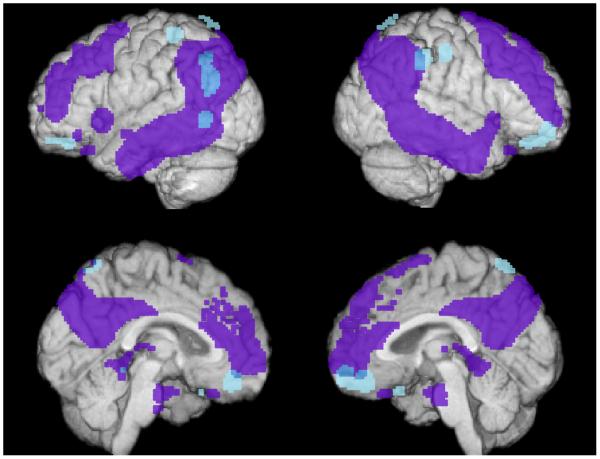
Figure 2. APOEε4 carriers with the protective GAB2 haplotype have higher regional-to-whole brain FDG uptake than APOEε4 non-carriers with the protective GAB2 haplotype in brain regions preferentially affected by AD.
Brain regions with higher regional-to-whole brain FDG uptake in APOEε4 carriers with the protective GAB2 haplotype than in APOEε4 non-carriers with the GAB2 protective haplotype (P<0.005, uncorrected for multiple comparisons) are shown in blue. Brain regions with lower CMRgI in previously studied probable AD patients versus controls (Alexander et al., 2002) are shown in purple. APOEε4 carriers with the protective GAB2 haplotype have higher regional-to-whole brain FDG uptake than APOEε4 non-carriers with the protective haplotype in regions outside of and overlapping with regions preferentially affected in patients with probably AD. These regions include the precuneus, and frontal, temporal, and parietal areas.