FIGURE 5. Vimentin is a novel AKT1 Kinase downstream target.
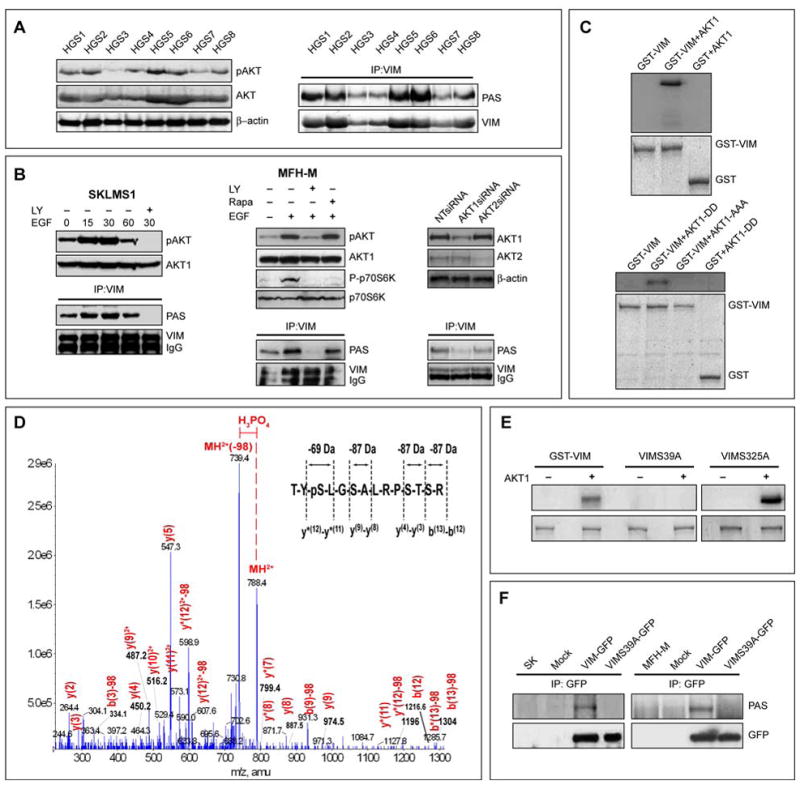
A. Primary human high grade STS (HGS 1-8) express pAKT (pS473; WB); Vim in these samples is recognized by the phospho-AKT substrate antibody (PAS antibody #9611, Cell Signaling; IP/WB) suggesting AKT-induced Vim phosphorylation; B. EGF induced pAKT enhances Vim phosphorylation in a time dependent manner in STS cells as indicated by increase in PAS detection on Vim. This effect was abrogated upon treatment with LY294002 but not by rapamycin. siRNA knockdown of AKT1 but to a lesser degree of AKT2 results in decreased Vim phosphorylation (demonstrated by Vim IP/PAS WB); C. An in vitro AKT1 kinase assay demonstrates the incorporation of [γ-32P]ATP into GST-VIM in the presence of activated AKT1 kinase but not AKT1 kinase dead protein (AKT1-AAA); D. An in vitro AKT1 kinase assay was performed in the presence of cold ATP and two bands corresponding to Vim treated with AKT1 or without AKT1 were subjected to mass spectrometry; shown is the product ion spectra for the of 2+ charge state of the TYSLGSALRPSTSR Vim peptide (788.39). LC/MS/MS data-dependent acquisition; the product ion spectra were searched against the Swissprot database using Mascot (Table S2). The 49 Da (2+) change designated in red indicates that a hydrogen phosphate group (HPO42-) and a water molecule (H2O) were lost from the peptide. y and b ions are indicated in red; the inset reveals a 69 Da change associated with the loss of a phospho-serine versus the 87 Da changes in ion mass associated with the loss of a non-phospho serine: E. In vitro AKT1 kinase assay demonstrated that constitutively activated AKT1 induces the phosphorylation of GST-VIM and GST-VIM-S325A but not GST-VIM-S39A; F. Anti-GFP IP after transfection of STS cells with either VIM-GFP or VIMS39A-GFP constructs demonstrated that Ser39 mutation abrogates AKT-induced Vim phosphorylation. [pAKT WB in all panels refer to pS473] (See also Figure S4)
