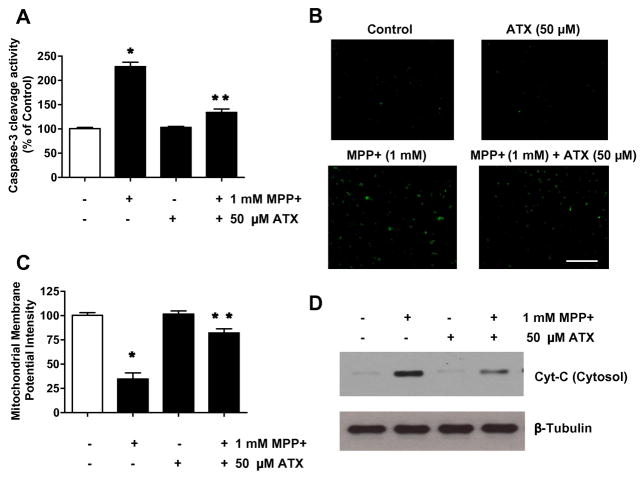
Fig. 5.
Effect of AST on MPP+-induced dysfunction of mitochondrial and caspase-3 activity in SH-SY5Ycells. Cells were treated with MPP+ (1 mM) for 24 h in the presence or absence of 50 μM AST. Enzymatic activity of caspase-3 (A), cleaved caspase-3 (active form of caspase-3)-positive cells (B), and mitochondrial membrane potential (C) were determined as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are from representative experiments repeated at least three times. Data are means ± S.E.M. (n = 3). *p < 0.05, compared with control (untreated cells); **p < 0.05, compared with the group treated by MPP+ alone. (D) Cytochrome c (15 kDa) release into cytosol was determined by immunoblotting for cytochrome c in the cytosolic fraction. Lysates containing equal amounts of protein (20 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-cytochrome c antibody. β-tubulin was shown as an internal standard.